18(51)
2. Structure Characteristics and Working Principle
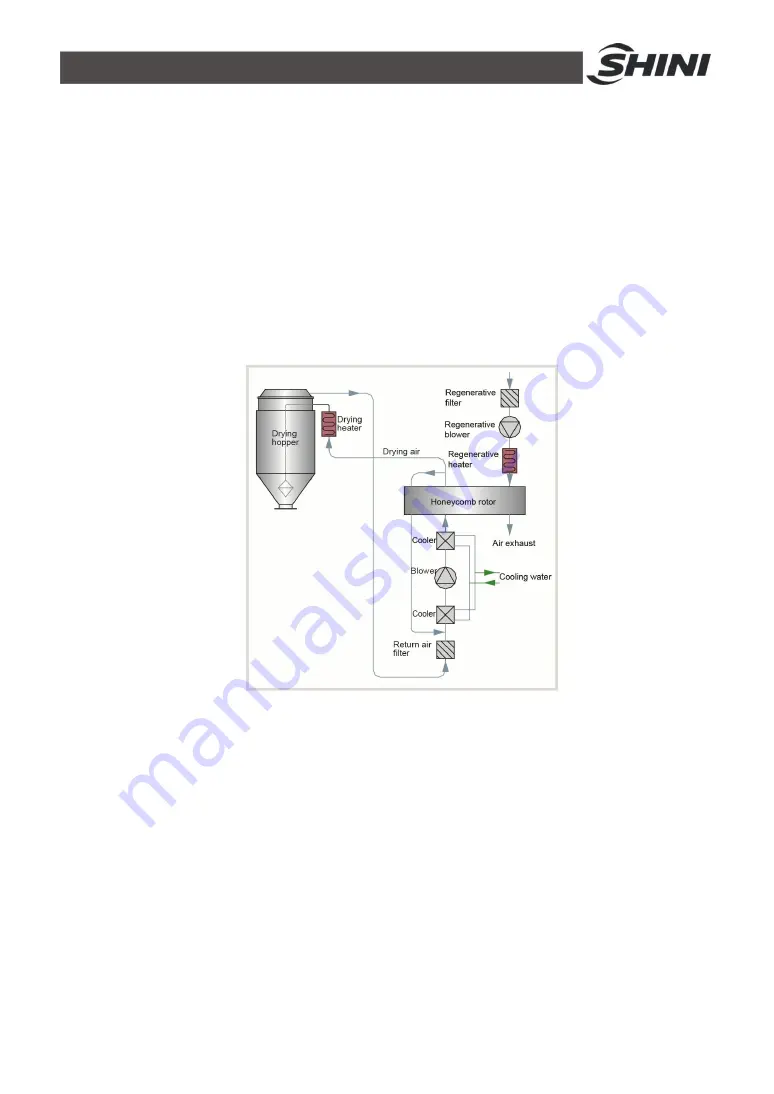
2.1 Working Principle
Moisture hot air from drying hopper is blown into rotor after flowing through cooler.
Moisture from the air is dried by rotor and is then adsorbed by regeneration
heating air. Two strands of airflow function on the rotor. And with the rotation,
moisture from the air is absorbed and expelled after absorbed regeneration air to
form stable low dew-point air, which is dried and heated to the drying temperature
and then is blown into material barrel to closed circle to dry material.
Picture 2-1: Working Principle
2.2 Relative Humidity and Dew-point
Relative humidity: Relative air humidity means real vapor content to saturated
vapor at the same temperature in percentage.
Dew point: it means that temperature when the saturation vapor begins to dew.
When the relative humidity is 100%, the ambient temperature is the dew point
temperature. The more lower of dew point temperature (than the ambient
temperature) is, the more less possible to dew, that also means the more drier the
air is. The dew point will not be influenced by temperature, but influenced by
pressure.






























