Chapter 3: Wiring
Firmware – S1043
Revision: 2 (9/98)
33
© Saftronics, Inc.
3.4.5
Wiring the Main Circuits
This section describes wiring connections for the main circuit inputs and outputs
§
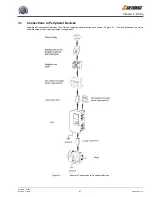
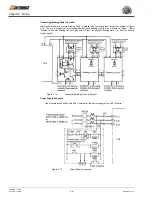
Wiring Main Circuit Inputs
Installing a Molded Case Circuit Breaker
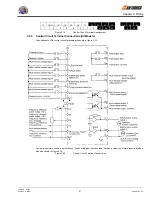
Always connect the power input Terminals L1, L2, and L3 (R, S, and T) and power supply via a Molded Case Circuit
Breaker (MCCB) suitable for the Inverter.
•
Choose an MCCB with a capacity of 1.5 to 2 times the Inverter’s rated current.
•
For the MCCB’s time characteristics, be sure to consider the Inverter’s overload protection (one minute at 150%
of the rated output current).
•
If the same MCCB is to be used for more than one Inverter, or other devices, set up a sequence so that the
power supply will be turned OFF by a fault output, as shown in
Figure 3.7.
VG5
*
For 400V class Inverters, connect a 400/200 V transformer.
Figure 3.7
MCCB Installation
Installing a Ground Fault Interrupter
Inverter outputs use high speed switching, so high-frequency leakage current is generated. Therefore, at the
Inverter primary side, use a ground fault interrupter that detects only the leakage current in the frequency range that
is hazardous to humans and excludes high-frequency leakage current.
•
For the special purpose ground fault interrupter for Inverters, choose a ground fault interrupter with a sensitivity
amperage of at least 30 mA per Inverter.
•
When using a general ground fault interrupter, choose a ground fault interrupter with a sensitivity amperage of
200 mA or more per Inverter and with an operating time of 0.1secondsor more.
Installing a Magnetic Contactor
If the power supply for the main circuit is to be shut off during a sequence, a
Magnetic Contactor can be used
instead of an MCCB.
When a Magnetic Contactor is installed on the primary side of the main circuit to forcibly stop the Inverter, however,
the regenerative braking does not work and the Inverter will coast to a stop.
•
The Inverter can be started and stopped by opening and closing the Magnetic Contactor on the primary side.
Frequently opening and closing the Magnetic Contactor, however, may cause the Inverter to break down.
•
When the Inverter is operated with the Digital Operator, automatic operation cannot be performed after recovery
from a power interruption.
•
If the Braking Resistor Unit is used, program the sequence so that the Magnetic Contactor is turned OFF by the
contact of the unit’s Thermal Overload Relay.
Connecting Input Power Supply to the Terminal Block
Input power supply can be connected to other Terminals L1, L2, and L3 (R, S or T) on the terminal block; the phase
sequence of input power supply is irrelevant to the phase sequence.