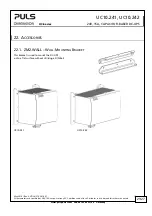
UC10.241, UC10.242
UC-Series
24V,
15A,
CAPACITOR-BASED
DC-UPS
11.
L
IFETIME
E
XPECTANCY AND
MTBF
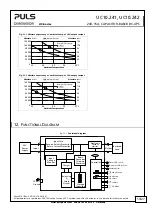
The lifetime expectancy of the DC-UPS is predominantly affected by the storage capacitors. The biggest influence in
lifetime is a combination of operating voltage and operating temperature of these capacitors. To gain longest
lifetimes, PULS does not utilize the full allowed working voltage for these capacitors and therefore accepts a slightly
shorter buffer time.
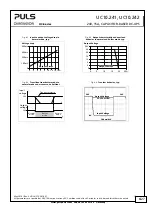
The EDLC’s do not experience a true end-of-life, rather the capacitance continually degrades over the life of the DC-
UPS. The typical degradation behavior resembles that of an exponential decay in the first couple of 1000 hours
followed by a linear degradation. The majority of the capacitance reduction occurs during the initial use of the DC-UPS
and this change in performance then levels off over time. When working with the specified lifetime numbers, the
remaining capacity must always be taken into account. The buffer time correlates linearly to the capacity.
The ultracapacitors have an almost unlimited shelf life (unlike batteries) when stored uncharged at 25°C.
The number of charge/ discharge cycles does not have an impact on the lifetime as long as the number of cycles does
not exceed 100 000. This should not be the case for a typical backup operation.
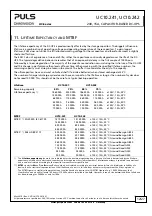
Lifetime UC10.241
UC10.242
Remaining capacity
85% 75% 85% 75%
Lifetime expectancy
*)
186 000h
324 000h
186 000h
324 000h
at 24V, 10A, 25°C
155 000h
270 000h
155 000h
270 000h
at 24V, 15A, 25°C
66 000h
115 000h
66 000h
115 000h
at 24V, 10A, 40°C
55 000h
96 000h
55 000h
96 000h
at 24V, 15A, 40°C
23 000h
40 000h
23 000h
40 000h
at 24V, 10A, 55°C
19 000h
34 000h
19 000h
34 000h
at 24V, 15A, 55°C
MTBF UC10.241
UC10.242
MTBF
**)
SN 29500, IEC 61709
1 519 000h
1 515 000h
at 24V, 10A, 25°C
1 443 000h
1 439 000h
at 24V, 15A, 25°C
899 000h
895 000h
at 24V, 10A, 40°C
854 000h
850 000h
at 24V, 15A, 40°C
MTBF
**)
MIL HDBK 217F
525 000h
524 000h
at 24V, 10A, 25°C; Ground Benign GB25
498 000h
497 000h
at 24V, 15A, 25°C; Ground Benign GB25
385 000h
384 000h
at 24V, 10A, 40°C; Ground Benign GB40
365 000h
364 000h
at 24V, 15A, 40°C; Ground Benign GB40
125 000h
125 000h
at 24V, 10A, 25°C; Ground Fixed GF25
118 000h
118 000h
at 24V, 15A, 25°C; Ground Fixed GF25
95 000h
95 000h
at 24V, 10A, 40°C; Ground Fixed GF40
90 000h
90 000h
at 24V, 10A, 40°C; Ground Fixed GF40
*) The
Lifetime expectancy
shown in the table indicates the minimum operating hours (service life) and is determined by the lifetime
expectancy of the built-in electrolytic capacitors and storage capacitors (ultracapacitors). Lifetime expectancy is specified in operational
hours and is calculated according to the capacitor’s manufacturer specification.
**)
MTBF
stands for
M
ean
T
ime
B
etween
F
ailure, which is calculated according to statistical device failures, and indicates reliability of a
device. It is the statistical representation of the likelihood of a unit to fail and does not necessarily represent the life of a product.
The MTBF figure is a statistical representation of the likelihood of a device to fail. A MTBF figure of e.g. 1 000 000h means that
statistically one unit will fail every 100 hours if 10 000 units are installed in the field. However, it can not be determined if the failed unit
has been running for 50 000h or only for 100h.
May 2016 / Rev. 2.2 DS-UC10.241-EN
All parameters are specified at 24V, 10A output current, 25°C ambient and after a 5 minutes run-in time unless otherwise noted.
www.pulspower.com Phone +49 89 9278 0 Germany
12/27