32
33
detail finer than the pixel size of
the frames being combined. The
technique is described at http://
xxx.lanl.gov/abs/astro-ph/9808087.
5.4. Filter
Filtering an image is an operation that
emphasizes certain characteristics of
an image while suppressing others.
MaxIm DL supports several kinds of
Filters, such as:
Unsharp Mask, Kernal
Filters, and Digital Development,
available from the
Filter menu.
Please read MaxIm DL’s
Help Topics
for the most detailed information about
the various image processing filters
available. The following are just some
of the many processing filters available
in MaxIm DL.
Unsharp Mask is a method of sharpening or high-pass filtering an image. It
amounts to subtracting a low-pass filtered version of an image from itself. The
low-pass filtered version is called the mask.
Kernal, High-Pass Filter can be set to More or Less for different effect. The High-
Pass Filter can be useful for accentuating fine details in an image.
Kernal, Gaussian Blur is a method of blurring an image. It can be used to sup-
press noise in an image at the expense of sharpness. The
Radius setting controls
the amount of blurring applied to the image. Increasing the radius increases the
amount of blur applied.
For best results, turn on the
Auto Full Screen preview button, and adjust the set-
tings. This allows you to rapidly adjust the settings until you are satisfied with the
results. Then, click
OK to actually apply the filter settings to the image.
It is best to use a light touch with this command, to avoid over-processing the
image. Over-processing can create artifacts; i.e. features in the image that are not
real. It also amplifies the noise in the image.
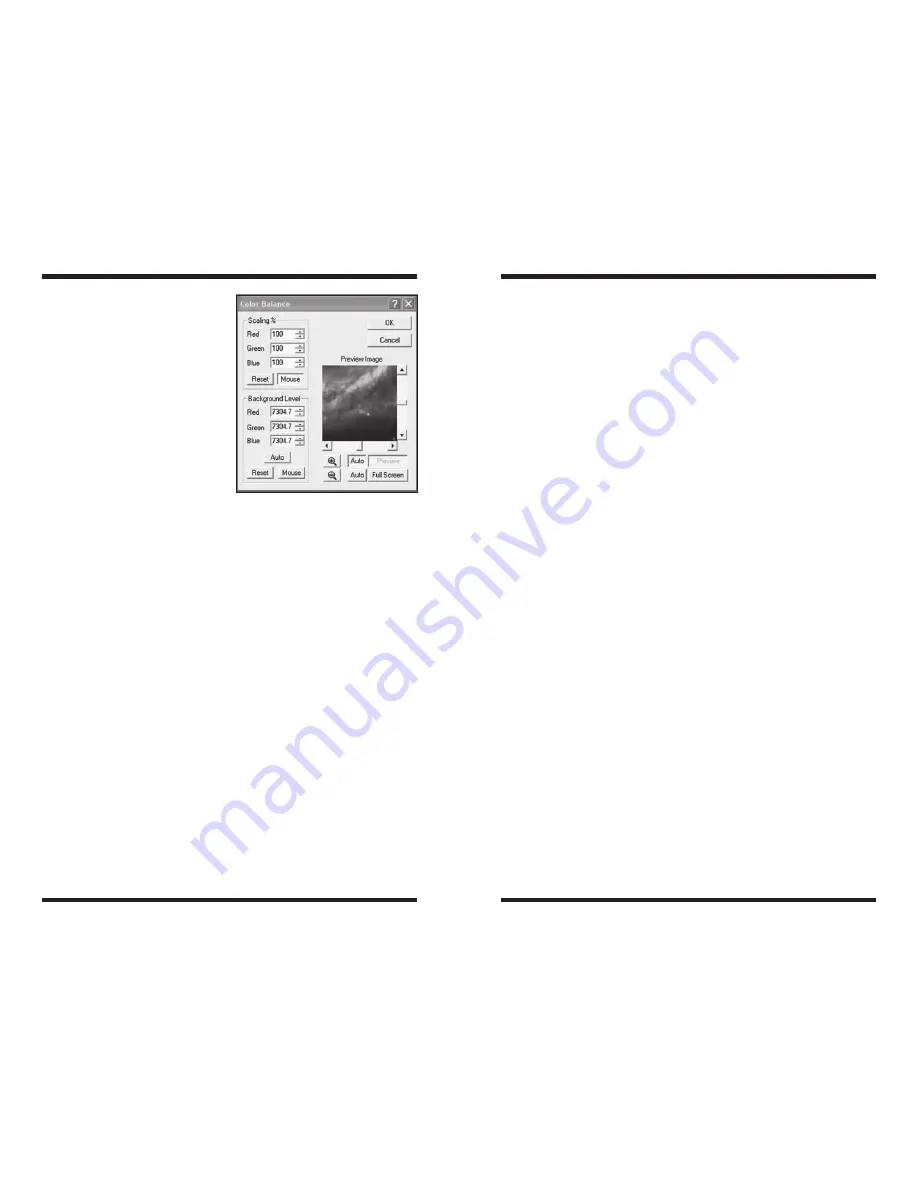
5.5. Color Balance
The sensitivity of most CCD cameras as a function of wavelength (color) is differ-
ent from the response of the human eye. The filters used for creating color com-
posites also have their own characteristics, as do the telescope optics. Although
“perfect” color rendition is an elusive if not impossible goal (all individuals see col-
ors slightly differently), it is straightforward to get “good” color balance with simple
weightings. This is where the
Color Balance command (in the Process menu,
Figure 31) comes in handy to touch up the resultant colors in your images. Use
the
Preview Image to see how altering these parameters will affect your image
(or click the
Full Screen button to see the changes applied to your full image).
Note for the Parsec 8300M: Before any color balance adjustment can be made,
you must first Combine Color to each individual LRGB or RGB images.
Color images from CCD cameras typically require a background level adjustment.
This is accomplished by bringing the background level (or bias) in each color plane
down to zero. Each of the
Background Level values is subtracted from every
image pixel in its color plane. Any pixel values that become negative are forced to
zero. The
Auto button automatically determines the settings necessary to equal-
ize the image background in all three color planes. The
Reset button resets the
background level subtraction to zero on all planes.
Scaling adjustment (entered as a percentage) allows you to compensate for
transmittance differences between the filters used to acquire the three color
planes. Values of 100% result in no change. The scaling percentages can be typed
in or adjusted using the “spin” controls (small up and down click arrows to the right
of the scaling numbers). The
Preview Image is particularly helpful in monitoring
the results when using the spin controls. The
Reset Scaling button resets to 100%
on all three planes.
The
Click On White Area to Set Scaling check box enables the operation of the
mouse to set the scaling. Set the
Background Level first (you can use Auto), then
click on a white object (e.g. a neutral-colored star) in the image (not the
Preview
Image) with the mouse. The Scaling settings will automatically be adjusted to
make the selected point appear white. If an area of the image is known to be white
(or gray), this is an easier way to determine the scaling factors, and can be used
to instantly color balance the image.
note on File Format
When saving individual images that were not taking during a sequence (using
Save or Save As in the File menu), you have a choice of file formats. The default
produces .fit files, but .tif, .jpg, .png, and .bmp file formats can also be selected.
Having a choice of output file formats is useful, especially if images will be
exported to other software programs for additional image processing (like Adobe
Photoshop, for instance).
If you save to a file format other than .fit, you will need to check the
Auto Stretch
box, or otherwise
Stretch the image to change the Output Range (in the Stretch
command window) to match the
Size Format (in the Save As window). Otherwise,
the
Output Range will likely exceed the Size Format, and the saved image will
be ruined (will turn all white).
For example, say the
Output Range is set to create image brightness values in
16-bit format, while the
Size Format of a specific file format (.jpg, for example)
may only support 8-bits. Since the 16-bit format sees 65535 brightness levels,
and the 8-bit format can only support 255 levels, all of the levels above 255 in the
16-bit image (i.e. the vast majority of the 16-bit brightness levels) will be saved at
the maximum 8-bit value of 255. So the saved .jpg will have very little brightness
Figure 31.
The
Color Balance
Window.






































