5.
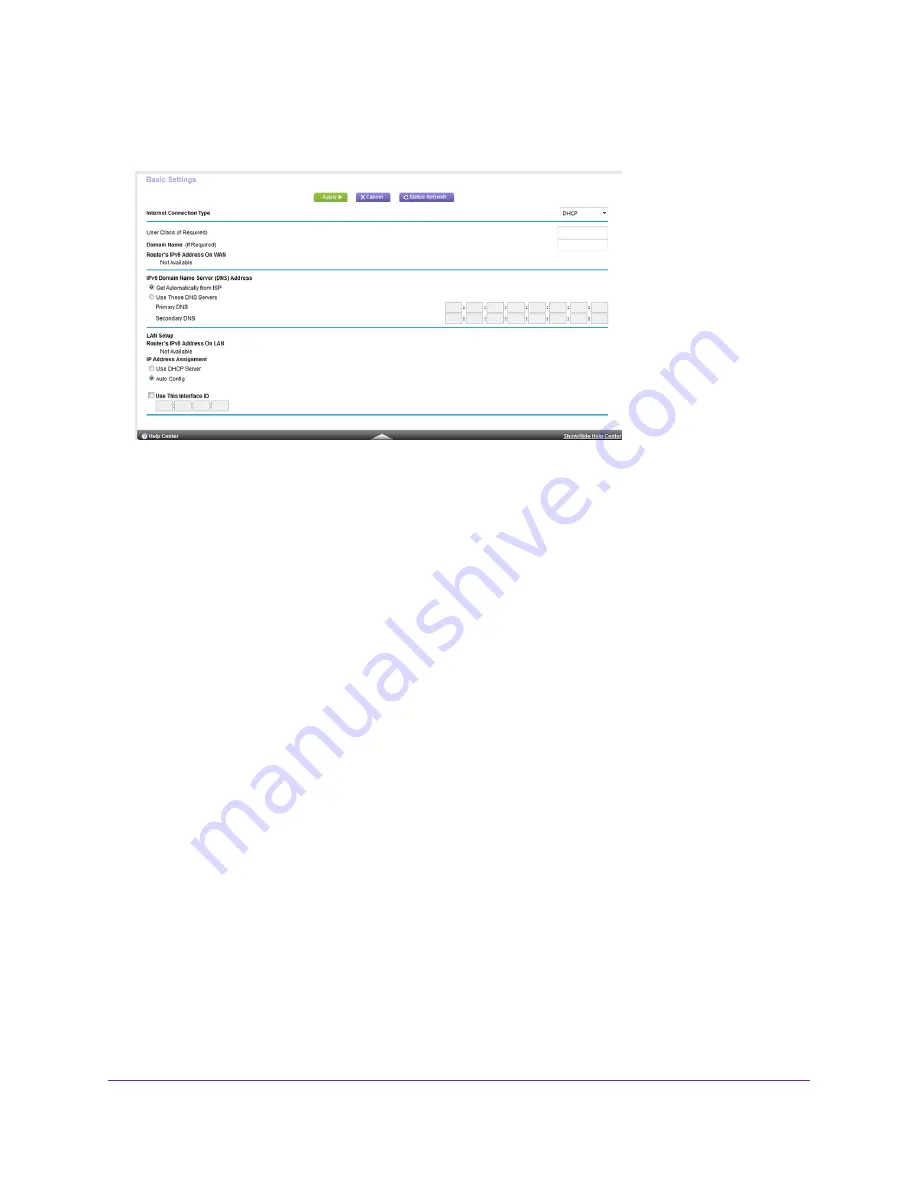
From the Internet Connection Type menu, select DHCP.
The router automatically detects the information in the following fields:
•
Router’s IPv6 Address on WAN. This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s WAN
(or Internet) interface. The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by
the underline (_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
•
Router’s IPv6 Address on LAN. This field shows the IPv6 address that is acquired for the router’s LAN
interface. The number after the slash (/) is the length of the prefix, which is also indicated by the underline
(_) under the IPv6 address. If no address is acquired, the field displays Not Available.
6.
(Optional) In the User Class (If Required) field, enter a host name.
Most people can leave this field blank, but if your ISP gave you a specific host name, enter it here.
7.
(Optional) In the Domain Name (If Required) field, enter a domain name.
You can type the domain name of your IPv6 ISP. Do not enter the domain name for the IPv4 ISP here. For
example, if your ISP’s mail server is mail.xxx.yyy.zzz, type xxx.yyy.zzz as the domain name. If your ISP provided
a domain name, type it in this field. For example, Earthlink Cable might require a host name of home, and
Comcast sometimes supplies a domain name.
8.
Select an IP Address Assignment radio button:
•
Use DHCP Server. This method passes more information to LAN devices but some IPv6 systems might not
support the DHCPv6 client function.
•
Auto Config. This is the default setting.
This setting specifies how the router assigns IPv6 addresses to the devices on your home network (the LAN).
9.
(Optional) Select the Use This Interface ID check box and specify the interface ID to be used for the IPv6
address of the router’s LAN interface.
Specify Your Internet Settings
35
















































