2
SuperScript Color Laser Network Guide
From Windows NT 4.0
•
If you have a NetWare network, see Chapter 6 for
Netware 5.x, 4.x, and 3.x configuration information.
•
In a Windows NT network you can use LPR printing. See
Chapter 5.
From Windows for Workgroups
•
If you have a NetWare network, see Chapter 6 for
Netware 5.x, 4.x, and 3.x configuration information.
•
You can also use shared printing, see Chapter 5.
From Mac OS
See Chapter 7 of this user’s guide to set up and print from
Macintosh computers over EtherTalk.
From Unix
See Chapter 8 for installing the printer on a UNIX system in
Solaris 2.x and SCO.
T
YPICAL
N
ETWORK
S
ETUPS
Typical Ethernet networks fall into basically three different
categories or topologies. Network topologies describe how a
network interconnects computers with other equipment such
as a printer. The following describes three topologies that can
be used as solutions for networking your printer. For web
printing options see Chapter 9.
Note:
In this user’s guide, the term “print client” means
a computer that can send a print job to the printer.
Types of Network Topologies
Three networking topologies can be used for networking
your SuperScript color laser printer.
•
Peer-to-Peer Topology
•
Printer Server Topology
•
Printer Sharing Topology
Peer-to-Peer Topology
Peer-to-peer topology is the simplest way to network your
printer. It involves print clients, a printer, and a network to
interconnect everything. The network operating system
(NOS) can be Microsoft NT Server, Novell NetWare, or
UNIX. Peer-to-peer is used primarily in smaller networks of
10 or fewer computers because peer-to-peer networking
software limits the number of users attached to any one
shared resource.
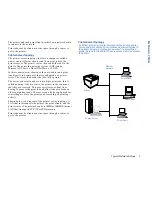
In this scenario,
print clients
use the network to send print
jobs directly to the printer. There is no intermediary
computer (server) that gets involved between the printer and
print clients.
Each client must compete with other clients for printer
availability. If the printer is busy processing a print job, each
client must store their jobs until the printer is ready to accept
them. However, the printer can be upgraded with more
memory to temporarily store multiple jobs until they are
printed. Shown below is an illustration of the peer-to-peer
topology.
A local area network (LAN) interconnects the printer and all
the print clients. The network can be a 10MB or 100MB
Ethernet LAN that transports TCP/IP or IPX protocols.
Ethernet
Network
Peer-to-Peer Topology
Printer
An Ethernet LAN is used to interconnect the printer and print clients.
Print clients send print jobs directly to the printer, but each must wait
for printer availability.
Print Client
Print Client