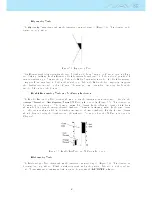
Wind Flag
The external circle contains a small ag which indicates the Wind Direction relative to the pilot direction
(direction the wind is coming from). For example, if the pilot is facing the wind then the ag is on the
top of the circle. In the example of (Figure
3.5
) the wind is blowing from Northeast.
3.1.6 Airspaces Map
The Airspaces Map element provides information to the user relative to specic three-dimensional objects,
previously loaded to the instrument. Each of this objects can be an airspace volume. Airspace information
can loaded to the instrument using the Flymaster Designer software (see Designer user manual for more
information). The NAV SD only accepts data in the OpenAir format, and it has a limitation of 12000
polygons points. (See
http://www.gdal.org/ogr/drv_openair.html
for more information about the
open air format).
Figure 3.9: Airspace Element
When the element of Figure
3.9
is inserted in a layout using DESIGNER, a 2D map (box) is shown on
the instrument (see Figure
3.10
). On the bottom left of the map the scale is indicated in Km, and on the
centre of the map is an arrow. This arrow represents the pilot position, and its orientation indicates the
bearing of the movement. The map is always oriented North Up.
Note: When new Airspaces data is uploaded to the NAV SD using DESIGNER the previews
data is deleted. If a empty Airspaces data le is uploaded then all the Airspaces will be deleted.
The rst time the map is drawn, it is centred on the last GPS position the NAV SD has in its memory.
The map is re-centred once the ight starts i.e. when a valid gps signal exists, and the start speed (see
Section
4.9.5
) is reached.
Note: After new Airspace data is uploaded to the NAV SD it can only be seen on the Map
after the Flight Starts.
Once the ight starts, the map is redrawn with an arrow (representing the pilot) which will move around
the map, indicating the relative position of the pilot to each of the airspace areas. If the pilot is outside
a visible airspace area then a gray line is used to draw the area, whereas if the pilot is inside the airspace
then a black line is used instead. Note that being inside a airspace area (2D) does not mean that the
airspace is being violated, since the pilot can be above, or below the dened 3D shape. In order to have
more information about possible airspaceÂs violation, some data elds should be added to the layout.
This data elds are Distance to CTR, Altitude to CTR, and CTR Status (Figure
3.10
).
The Dist. CTR data eld shows the shortest horizontal distance to the nearest airspace line. This distance
is always positive. Similarly, the Alt. To CTR shows the shortest vertical distance to nearest airspace line.
Unlike the horizontal distance, the vertical distance can be negative. A positive vertical distance indicates
that you are outside the airspace, whereas a negative distance indicates that you are inside the airspace.
Additionally, the CTR status eld will indicate if an airspace is being violated by displaying Violating.
If the pilot is not violating the airspace but it is inside a predened margin then the messages Altitude
Imminent, or Position Imminent will be shown.
13
Summary of Contents for Flymaster NAV SD
Page 1: ...User manual Version 3 0...
Page 54: ...Figure 4 42 GPS Reset 53...