Page 22
5.6 EEG analysis for children in the first year of life
The analysability of anesthesia EEGs registered for children in the first months of life,
will depend to a large extent on the children's level of development. Appearing from the
age of approximately three months until the age of 12 months in an increasing number
of children, are typical EEG anesthesia stages, which can be classified visually and
automatically.
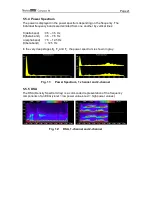
EEG classification among children under the age of 60 days
For this age group only EEG classifications for stages with implied or clear suppression
lines (E
2
to F
1
) are displayed. The scale of the cerebrogram is designed accordingly.
If there is an EEG without suppression lines, the output is “Undiff. EEG”. This stands for
“undifferentiated EEG”.
EEG classification among children between the age of 60 days and the age of 1
For children of this age the full A-F scale is displayed on the left side of the cerebrogram
window.
From the outset of measurements the EEG is analysed for certain attributes, which
suggest a mature and thus fully classifiable EEG.
As long as no fully classifiable EEG is detected, instead of an indication of stage or
index, the output “Undiff. EEG” is displayed in the index field, if the raw EEG shows no
sign of suppression lines. If the EEG has been graded as classifiable, from now on
classifications can also be outputted throughout the stages E
2
to F
1
.