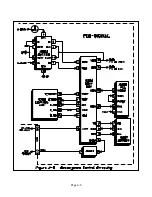
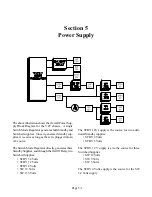
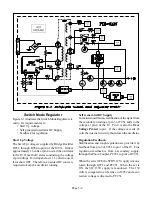
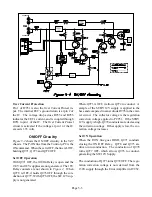
Page 6-6
SHORT Circuit
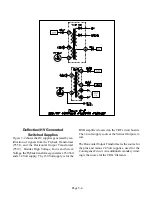
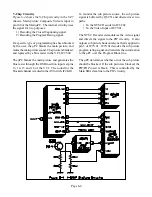
Figure 6-7 shows the SHORT circuitry. The input
at pin 46 of IC700, connects to the 5V Standby Sup-
ply through R7B19. Three Switched Supplies are
monitored through discrete diodes. Under normal
conditions, all the diodes are reversed biased and pin
46 is HIGH from the 5V supply.
If a short is present on any of the monitored sup-
plies, that specific diode is forward biased pulling
pin 46 LOW. The uPC responds by automatically
shutting the set OFF.
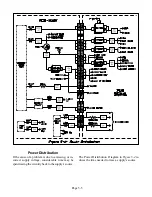
The SHORT line also monitors the Horizontal Out-
put transistor, and the Horizontal Yokes' current.
R566 is the ground return for both Q5A00 and the
Horizontal Yokes. If current through R566 becomes
excessive, the increased voltage turns Q533 ON. The
conduction of Q533 pulls the SHORT line LOW,
shutting the TV OFF.
The three main causes resulting in excessive voltage
across R566 are:
1) Shorted or leaky Horizontal Output Transis-
tor.
2) Shorted Horizontal Deflection Yoke.
3) Excessive current drain on the Convergence
+ 24 Volt DC Supplies, generated from T519
in the collector circuit of Q5A00.
X-RAY Protect
Figure 6-8 illustrates the X-
RAY Protect circuitry. The
logic at pin 47 of the uPC is
controlled by two protect cir-
cuits, monitoring for excess
HV and Beam Current.
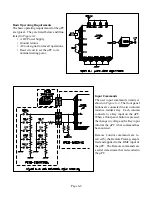
To monitor HV, a sample of
the HV is derived from the
resistive divider in the CR
Block, and is directed to pin
5 of IC501. The sample is
amplified in IC501 and di-
rected to the inverting input
of an OP Amplifier at pin 6
of IC502. A stable reference voltage, from IC503,
is applied to the non-inverting input of the OP Am-
plifier, pin 5.
If HV becomes excessive, the sample at pin 6 of
IC502, exceeds the reference voltage at pin 5, and
the output at pin 7 goes LOW. The uPC responds to
the LOW on the X-RAY line by switching the set
OFF.
To check if the excess HV Protect is working, short
pins 1 and 2 of the DN connector. If the TV does
not shut off, a circuit problem exists.
Beam Current Protect
Beam Current is detected by monitoring the voltage
at the Flyback HV Winding ground return, pin 8 of
T551. The voltage at pin 8 drops as beam current
increases. If the drop in voltage is excessive, D543
is forward biased, dropping the voltage at pin 3 of
IC502. If the voltage at pin 3 drops below the refer-
ence at pin 2, the output at pin 1 goes LOW, pulling
the X-RAY line LOW.
To check the Beam Current Protect circuit, short
pins 1 and 3 of the DQ connector. The TV must
shut off. Failure to shut off indicates a circuit prob-
lem.
Summary of Contents for VS-45605
Page 11: ...Page 1 8 ...
Page 25: ...Page 3 10 ...
Page 27: ...Page 4 2 ...
Page 31: ...Page 4 6 ...
Page 33: ...Page 4 8 ...
Page 55: ...Page 8 8 ...
Page 57: ...Page 7 2 ...
Page 69: ...Page 9 2 ...