71
70
15.5.5 CLASS
a) Non-cohesive with grain size from 100 to 250 mm in more than 50% of volume of the rock to be separated, with grain size
above 250 mm up to 0,1 m3 individually in more than 10% up to 50% of volume of the rock to be separated (coarse gravel
with stone/boulders);
b) Non-cohesive, classified in Class 4, held together by a cohesive material with Class 4 properties, as far as their grains
remain in lumps after separation (coarse gravel with clay-loam bonding material);
c) Solid, healthy, in layers up to 150 mm thick (conglomerate with clay bonding material, slate, travertine, sandy marlstone,
etc.);
d) Solid, igneous, sedimentary, weathered and cracked with areas of divisibility of less than 150 mm (weathered granite,
gneiss, andesite, sandstone, quartz);
e) Landfill materials similar in nature to Class 5 rocks;
f) Frozen soils.
15.6.6 CLASS
a) Non-cohesive with boulders from 250 mm up to 0,1 m3 individually in more than 50% of volume of the rock to be sepa-
rated, with boulders above 0,1 m3 individually in up to 50% of volume of the rock to be separated;
b) Solid, igneous and metamorphic rocks, healthy with areas of divisibility up to 1.0 m in bench block separation. Crack dis-
tances less than 250 mm (granite, gneiss, andesite, basalt, slate, phyllite);
c) Firmly sedimented, healthy with a distance of divisible surfaces up to 1.0 m. Other crack distances of up to 250 mm -
coarsely bench-shaped (coarsely fragmentary to boulder conglomerates and agglomerates with calcareous and marly
bonding material, limestones, dolomite, etc.).
15.7.7 CLASS
a) Non-cohesive with grain size over 0.1 m3 individually in more than 50% of volume of the rock to be separated;
b) Solid, healthy, massive, or with irregular spherical, columnar detachment with individual wedges, with areas of divisibility
greater than 250 mm (quartz, silica granite, gneiss, basalt, andesite, veined quartz, cherty limestones, diorites).
Abbreviated characteristics of the mining classes according to the ways in which rocks can be separated:
Class 1 - loose rocks that can be picked up with a shovel/with loader;
Class 2 - excavable rocks, separable with a spade/with loader;
Class 3 - diggable rocks, separable with a pickaxe/with excavator;
Class 4 - crumbly solid rocks, separable with a wedge/with excavator;
Class 5 - solid rocks that are easily broken up and separable with a ripper/heavy excavator (over 40 tons) or with explosives;
Class 6 - solid rocks that are difficult to break up with a heavy ripper or with explosives;
Class 7 - solid rocks that are very difficult to break up, separable with explosives.
16. REMOVING / INSERTING THE BATTERY
16.1 REMOVING THE BATTERY FROM THE MACHINE
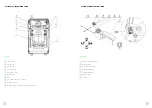
Open the machine top cover (position 1).
Open the machine bottom cover (position 2).
Disengage the battery connector (position 3).
Unlock the battery levers (position 4).
Slide the frame for battery replacement (position 5) onto the pallet truck (position 6) and fix it with chain.
Slide the pallet truck with the frame under the machine battery (position 7) and carefully pull out the battery.
Connect the battery to a charger that is in its designated place.
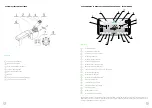
16.2 INSERTING THE BATTERY INTO THE MACHINE
Using a pallet truck (position 6) and the frame for battery replacement (position 5), carefully insert the battery
into the machine.
Lock the battery levers (position 4).
Attach the battery connector (position 3).
Close the machine bottom cover (position 2).
Close the machine top cover (position 1).
Picture 61
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
3
4
5