To be certain that the quality of the data is of a high standard, care must be taken with daily maintenance of the pyrgeometer.
Once a voltage measurement is taken, nothing can be done to retrospectively improve the quality of that measurement.
During field measurements the pyrgeometer is exposed to varying atmospheric conditions with typical radiating properties.
Therefore we define the two most common conditions as ‘overcast sky’ and ‘clear sky’.
2.4.1 Overcast sky
Typical for a cloudy overcast sky is that radiation emitted by the earth is absorbed 100% by the clouds. Therefore, the overcast
sky will re-emit the radiation (
L
d↓
) 100%.
In theory, the net radiation (U
emf
/S) will be zero, so the pyrgeometer detector output voltage (U
emf
) will be zero. In practice,
the detector output shows a small negative voltage (a few W/m²), due to a small heat exchange between the relatively warm
pyrgeometer and the colder sky.
In this case the calculated atmospheric long-wave radiation (
L
d↓
) shows a relatively large positive value. In the case of rain, the
detector output will read zero, because water deposited on the pyrgeometer window is a perfect infrared absorber.
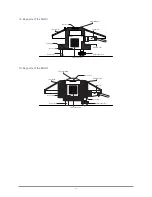
Cloudy overcast sky condition
2.4.2 Clear sky
Clear sky conditions differ in that there is a relatively large heat loss caused by the atmospheric window. The amount of
re-emitted radiation by a clear sky is smaller compared to the overcast sky condition. Because of the heat loss in the upward
direction, the thermopile hot junctions will cool down and show a relatively large negative net radiation value (from -90 to
-130 W/m²). Therefore, the calculated atmospheric long-wave radiation (
L
d↓
) shows a relative small positive value.
Clear sky condition
Atmosphere T
atm
Earth’s surface T
earth
>T
atm
Net radiation
(-90 to -130 W/m
2
)
Downward radiation
(Relatively small value)
Upward radiation
Atmosphere T
atm
Earth’s surface T
earth
>T
atm
Net radiation
(0 to -5 W/m
2
)
Downward radiation
(Relatively large value)
Upward radiation
19