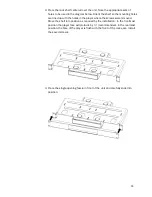
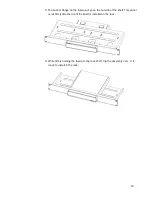
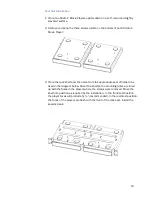
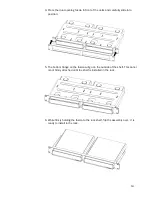
22
About HDR
High dynamic range (HDR) content incorporates both a wider color gamut
–
meaning that it can display more vivid and lifelike colors
–
and the ability to
display very bright and very dark images simultaneously. This combination
produces remarkably realistic images.
Strato C fully supports 10-bit 4K HDR content, at up to 60 frames per second,
provided that Strato C is connected to a display that supports 4K HDR. As of
2017, new 4K displays typically all support HDR. HDR support is less common
in older displays.
See the Supported 4K Ultra HD Modes section on page 26 to learn how Strato C
can help you discover the capabilities of the connected display.
About Chroma Sampling
In addition to bit depth, another factor in how images are displayed is how the
color information is represented. This is usually expressed in terms of three
numbers separated by colons, like 4:4:4 or 4:2:0.
The details of this notation are beyond the scope of this document, but in
summary, 4:4:4 has discrete
luma
(brightness) and
chroma
(color) information
for every pixel in an image. 4:2:0 has discrete luma for every pixel, but the
chroma is averaged across 2x2 clusters of pixels.
4:2:0 significantly reduces the amount of data required for each frame, so a
4:2:0 signal requires less bandwidth than a 4:4:4 signal. In a moving image,
the difference in chroma resolution is not perceptible to most viewers.
4K Ultra HD movie content is encoded as 4:2:0 (as are Blu-ray and DVD discs
and Blu-ray quality and DVD quality downloads), so a 4:2:0 connection does not
compromise video playback quality.
The Kaleidescape onscreen display can be rendered with 4:4:4 color sampling
on displays that support it, if the HDMI connection supports 18 Gbps. This will
produce the most detail when looking at images in the onscreen display, such
as the Movie Covers view.