S p e z i a l e l e k t r o n i k G m b H
iseg Spezialelektronik GmbH
Email: [email protected]
Tel ++ 49 (0)351 / 26 996 - 0
Bautzner Landstr. 23
http://www.iseg-hv.de
Fax ++ 49 (0)351 / 26 996 - 21
22
D - 01454 Radeberg/ Rossendorf
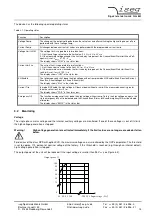
C:\>ping 192.168.16.13
Ping will done for 192.168.16.13 with 32 bytes data:
Answer from 192.168.16.13: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
Answer from 192.168.16.13: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
Answer from 192.168.16.13: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
Answer from 192.168.16.13: bytes=32 time=4ms TTL=128
Ping statistic for 192.168.16.13:
Package: sent = 4, received = 4, lost = 0
Time in millisecond:
minimum = 1ms, maximum = 4ms, average = 1ms
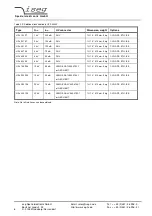
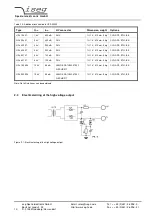
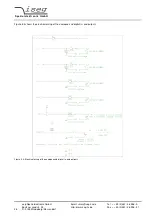
During communication the HV unit act as server, the control PC act as client. The following table shows the principle sequence
of communication PC to HV unit.
Step
Function call
Computer HV-Unit
HV-Unit Computer
1.
connect()
SYN
2.
SYN, ACK
3.
ACK
4.
send()
"*IDN?\r\n"
5.
recv()
"iseg Spezialelektronik GmbH [...]"
6.
closesocket()
FIN, ACK
7.
FIN, ACK
8.
ACK
The first three packages are for the establishing of a TCP-Connection (three way handshake). Fourth step is the inquiry from
PC to HV unit. The order is ASCII coded in data field of the TCP packet. The answer is also ASCII coded send to the PC in
step 5. Package No. 6 confirms the receipt of the packet and sends a FIN for termination of connection. Step 7 and 8 are the
confirmation of termination of connection from HV unit and PC.
The communication can be monitored with a network sniffer (e. g. Wireshark). Control is done with the instruction sets de-
scribed later. The preferred command set for Ethernet is “SCPI with EDCP”, as you can build longer Frames which reduces
Ethernet Overhead.