6-18
Entering and Evaluating Equations
Th
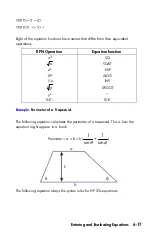
e next equation also obeys the syntax rules. This equation uses the inverse
function,
, instead of the fractional form,
. Notice that
the SIN function is "nested" inside the INV function. (INV is typed by
.)
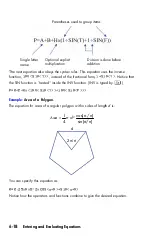
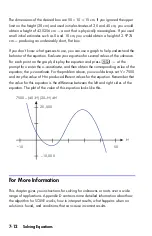
Example:
Area of a Polygon.
The equation for area of a regular polygon with
n
sides of length
d
is:
Area
=
You can specify this equation as
π
π
Notice how the operators and functions combine to give the desired equation.
Parentheses used to group items
Single letter
name
Optional explicit
multiplication
Division is done before
addition
/n)
sin(
)
/
cos(
4
1
π
π
n
n d
2
d
2 /n
π
Summary of Contents for 35s
Page 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Page 14: ...12 Contents ...
Page 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Page 16: ......
Page 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Page 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Page 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Page 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Page 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Page 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Page 182: ......
Page 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Page 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Page 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Page 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Page 286: ......
Page 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Page 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Page 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Page 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Page 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Page 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Page 382: ...Index 12 ...