3-2
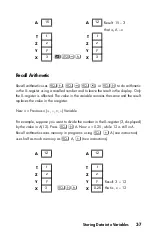
In ALG mode, you can store an expression into a variable; in this case, the value of
the expression is stored in the variable rather than the expression itself.
Example:
Each pink letter is associated with a key and a unique variable. (The
A..Z
annunciator in the display confirms this.)
Note that the variables,
X
,
Y
,
Z
and
T
are
different
storage locations from the X–
register, Y–register, Z–register, and T–register in the stack.
Storing and Recalling Numbers
Numbers and vectors are stored into, and recalled from, lettered variables by
means of the Store (
) and Recall (
) commands. Numbers may be
real or complex, decimal or fraction, base 10 or other as supported by the HP 35s.
To store a copy of a displayed number (X–register) to a direct variable:
Press
letter–key
.
To recall a copy of a number from a direct variable to the display:
Press
letter–key
.
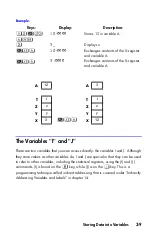
Example:
Storing Numbers
.
Store Avogadro's number (approximately 6.0221
×
10
23
) in
A
.
Keys:
Display:
Description:
Enter the expression, then
proceed as in the previous
example.
Summary of Contents for 35s
Page 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Page 14: ...12 Contents ...
Page 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Page 16: ......
Page 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Page 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Page 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Page 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Page 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Page 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Page 182: ......
Page 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Page 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Page 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Page 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Page 286: ......
Page 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Page 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Page 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Page 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Page 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Page 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Page 382: ...Index 12 ...