2-2
RPN: The Automatic Memory Stack
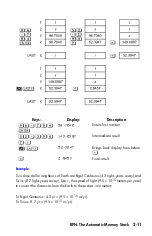
The most "recent" number is in the X–register:
this is the number you see in the
second line of the display.
Every register is separated into three parts:
A real number or a 1-D vector will occupy part 1; part 2 and part 3 will be
null in this case
.
A complex number or a 2-D vector will occupy part 1 and part 2; part 3 will
be null in this case
.
A 3-D vector will occupy part 1, part 2, and part 3
.
In programming, the stack is used to perform calculations, to temporarily store
intermediate results, to pass stored data (variables) among programs and
subroutines, to accept input, and to deliver output.
T
P a r t 3
“ O l d e s t ” n u m b e r
P a r t 2
P a r t 1 0
.
0 0 0 0
Z
P a r t 3
P a r t 2
P a r t 1 0
.
0 0 0 0
Y
P a r t 3
D i s p l a y e d
P a r t 2
P a r t 1 0
.
0 0 0 0
X
P a r t 3
D i s p l a y e d
P a r t 2
P a r t 1 0
.
0 0 0 0
Summary of Contents for 35s
Page 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Page 14: ...12 Contents ...
Page 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Page 16: ......
Page 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Page 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Page 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Page 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Page 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Page 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Page 182: ......
Page 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Page 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Page 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Page 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Page 286: ......
Page 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Page 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Page 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Page 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Page 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Page 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Page 382: ...Index 12 ...