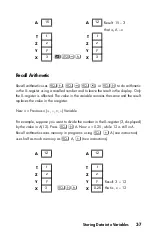
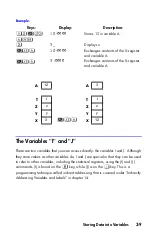
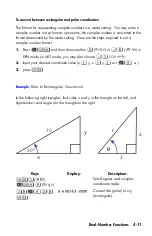
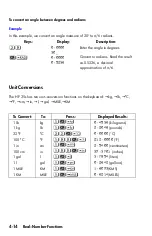
4-4
Setting the Angular Mode
The angular mode specifies which unit of measure to assume for angles used in
trigonometric functions. The mode does
not
convert numbers already present (see
"Conversion Functions" later in this chapter).
360 degrees = 2
π
radians = 400 grads
To set an angular mode, press
9
. A menu will be displayed from which you
can select an option.
Trigonometric Functions
With
x
in the display:
Option
Description
Annunciator
Sets degree mode, which uses decimal
degrees rather than hexagesimal degrees
(degrees, minutes, seconds)
none
Sets radian mode
RAD
Sets gradient mode
GRAD
To Calculate:
Press:
Sine of
x
.
Cosine of
x
.
Tangent of
x
.
Arc sine of
x
.
Arc cosine of
x
.
Arc tangent of
x
.
Note
Calculations with the irrational number
π
cannot be expressed
exactly
by the 15–digit internal precision of the calculator. This is
particularly noticeable in trigonometry. For example, the
calculated sin
π
(radians) is not zero but –2.0676
×
10
–13
, a very
small number close to zero.
Summary of Contents for 35s
Page 1: ...HP 35s scientific calculator user s guide H Edition 1 HP part number F2215AA 90001 ...
Page 14: ...12 Contents ...
Page 15: ...Part 1 Basic Operation ...
Page 16: ......
Page 46: ...1 30 Getting Started ...
Page 63: ...RPN The Automatic Memory Stack 2 17 A Solution ...
Page 64: ...2 18 RPN The Automatic Memory Stack ...
Page 74: ...3 10 Storing Data into Variables ...
Page 180: ...12 14 Statistical Operations ...
Page 181: ...Part 2 Programming ...
Page 182: ......
Page 246: ...15 12 Solving and Integrating Programs ...
Page 270: ...16 24 Statistics Programs ...
Page 284: ...17 14 Miscellaneous Programs and Equations ...
Page 285: ...Part 3 Appendixes and Reference ...
Page 286: ......
Page 308: ...B 8 User Memory and the Stack ...
Page 322: ...C 14 ALG Summary ...
Page 336: ...D 14 More about Solving ...
Page 346: ...E 10 More about Integration ...
Page 352: ...F 6 Messages ...
Page 370: ...G 18 Operation Index ...
Page 382: ...Index 12 ...