– 50 –
How It Works
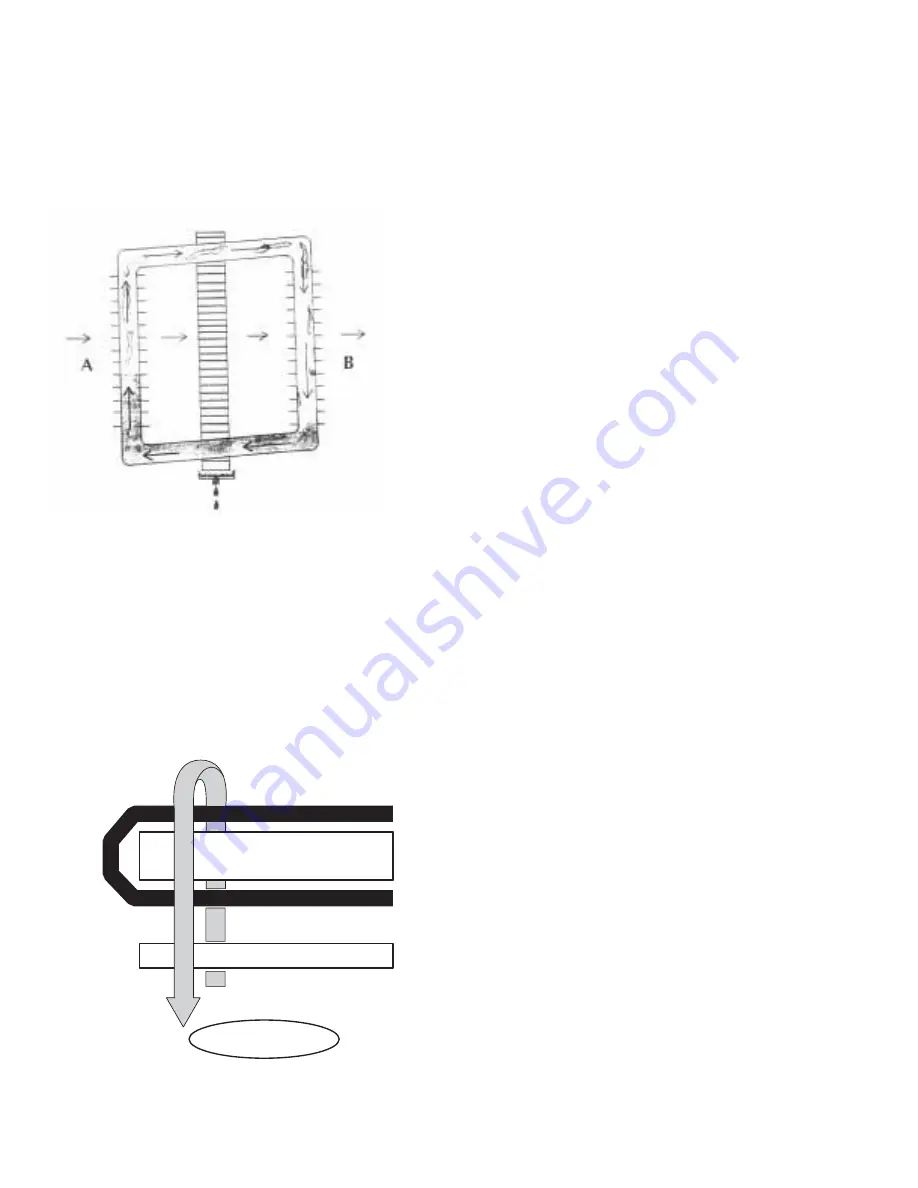
When the air enters the unit it passes through the
front coil of the heat pipe saddlebag. As the air
passes through the heat pipe, the heat in the air
causes the refrigerant in the heat pipe to boil or
vaporize into a gas.
The gas rises and fl ows through the connecting
tubing to the rear of the heat pipe. At this point,
the dry bulb temperature of the air is reduced as it
passes through the front coil of the heat pipe. As
the precooled air passes through the evaporator
it allows the evaporator to operate at a lower
temperature and the unit is able to remove a
signifi cantly greater amount of moisture from the
air.
HEAT
PIPE
ASSY
AIR FILTER
ROOM AIR
EVAPORATOR COIL
80˚F
71.5˚F
46˚F
54.6˚F
EVAPORATOR
PRECOOL
HEAT PIPE
REHEAT
HEAT PIPE
When the air leaves the evaporator it is over-cooled
and greatly dehumidifi ed. As the air passes through
the rear coil of the heat pipe, the same amount of
heat is transferred to the air as was removed when
the air passed through the front coil. This transfer
of heat causes the refrigerant in the rear coil of
the heat pipe to condense back into a liquid. It
then fl ows downward (by gravity) in the heat pipe
connecting tubing and back to the front coil of the
heat pipe. The result is a discharge air temperature
about the same as the discharge air temperature
of a unit without the heat pipe, but the relative
humidity is considerably lower.
Heat Pipe - Resistance Heat Operation
Heat Pipe is available only on the 2800 series, which
uses resistance heat. Since the refrigerant system
is not operating during the heat mode, there is no
condensing of moisture occurring. The heater is
located after the heat pipe and therefore has no
effect on the refrigerant in the heat pipe.
Available Heat Pipe Models
Heat Pipe, also referred to as Dry Air, is available on
6 models in the 2800 series. Models using 230/208
VAC with 7000, 9000 and 12000 BTUs of cooling
and 2.55/2.09 KW and 3.45/2.82 KW of heat. Models
using 265 VAC with 7000, 9000, and 12000 BTUs
of cooling and 1.0, 1.55, and 2.45 KW of heat. Dry
Air (heat pipe) models will also have a “P” in the
last character of the model number, example,
AZ28E07DAP. The Dry Air models have the corrosion
protected chassis because these units are designed
for coastal applications and in areas that have
relatively high humidity.
Diagnosing Potential Heat Pipe Problems
The heat pipe coil is fi eld-repairable. Take off
the front cover, the left side of the heat pipe is
accessible with the grille off. With the unit running
in the cool mode (make sure the indoor fan motor
is running) use your hand and feel each pass of the
coil. The bottom of each heat pipe coil should be
cooler (cool vapor refrigerant) than the top of the
heat pipe coil (heated liquid refrigerant) by a few
degrees. If there is no temperature difference on the
coil being checked (room temperature), chances are
that the coil has lost its refrigerant charge.











































