26 / 48
Festo 7DGE_25-63_ZR_KFb_en
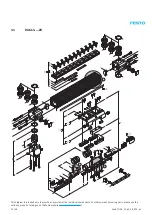
4.4
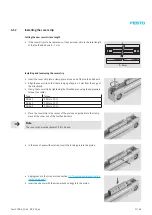
Replacing the toothed belt
If the toothed belt has to be changed, the cause of the failure must be investigated to prevent premature and repeated
failure. A toothed belt axis that has been used as intended and sized correctly will not normally exhibit any premature
signs of failure.
This is not necessary in the case of non-premature failure (fatigue time). However, the condition of the toothed drive shaft
(wear to the surface/shape of the teeth, radial play of the bearing inner raceway with respect to the bearing seat: tight fit
in new condition) and also the condition of the deep-groove ball bearings (e.g. perceptible bearing clearance, impaired
roll-off behaviour and increased operating noise, etc.) should always be checked. In case of uncertainty, it is recommend-
ed to replace all the components mentioned so as to rule out reciprocal effects during later operation.
Possible visible signs of wear to the toothed belt:
• Tears on the back of the toothed belt are signs of wear, for example caused by operation outside the permitted tem-
perature range, impermissible chemical influences or possibly fatigue.
• Wear to the nylon fabric (fabric coating) on the tooth side of the belt. This is indicated by lint formation and bobbling,
for example, and constitutes primary wear (abrasion of the fabric).
• Visible individual glass fibre tensile strands in the tooth base are secondary signs of wear due to primary wear to
the nylon fabric. If this happens, the toothed drive shaft must be carefully examined for wear since visible glass fibre
tensile strands may have had a severe abrasive effect on the tooth tip sides of the toothed belt pulleys.
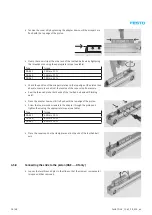
A description of how to replace the toothed drive shafts together with the corresponding deep-groove ball bearings can
be found in section
If the toothed belt suffers premature failure, the operating conditions should be looked at more closely.
The following possibilities should be considered among others:
• Overloading
The elasticity of the toothed belt retards the acceleration and braking behaviour of the toothed belt axis and results
in greater acceleration and deceleration than set in the controller (spring effect).
Block-shaped acceleration and deceleration profiles (no jerk limitation) cause high peaks in the drive force that can
lead to overloading of the drive. Positions outside of the permissible range can also occur. An acceleration and de-
celeration specification with jerk limitation reduces oscillations in the entire system and has a positive effect on the
stresses to which the mechanical system is subjected.
– Check which closed-loop controller settings can be adapted (e.g. jerk limitation, smoothing of the acceleration
profile).
Incorrect set values for the braking ramp during STOP conditions (e.g. emergency stop, quick stop) result in overload-
ing of the toothed belt axis and can destroy it or dramatically reduce its service life.
– Check the settings for all braking ramps in your controller or the higher-order control system (deceleration values
and jerk).
– Make sure that the deceleration values (braking deceleration, deceleration times) for the speed, the load to be
moved and the mounting position (horizontal/vertical) as well as the specified maximum driving torque or the
feed force correspond to the permissible values for the toothed belt axis used.
– Use the Festo “Positioning Drives” sizing software, available via the Festo website (
www.Festo.com
), to size the
toothed belt axis.
• Ambient conditions/material resistance
Check whether the ambient temperature is within the permissible range.
Check the chemical and physical ambient conditions for hazardous substances such as dust, abrasive particles, cool-
ing lubricants, solvents, ozone, radiation, water-soluble greases and oils, etc.
The toothed belt is ordered from the online spare parts catalogue (
) using the appropriate part
number (dependent on the size and version of the toothed belt axis).
The part number is an x-stroke part number. You must specify the stroke of your toothed belt axis in addition to the part
number when ordering. The stroke can be determined from the type codes on the name plate of the toothed belt axis (see
order example below). You can use this information to calculate the necessary toothed belt length.
Summary of Contents for DGE-25 ZR RF Series
Page 47: ......
Page 48: ......
Page 49: ...Operating instructions en Toothed belt pretension test equipment 7Tension01_TBb_en...