Megadisk NAS Owner’s Manual
37
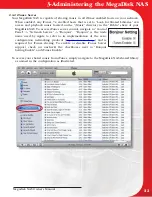
RAID 10
A RAID 10 array is formed using a two-layer hierarchy of RAID types. At the lowest level
of the hierarchy are a set of RAID 1 arrays i.e., mirrored sets. These RAID 1 arrays in turn are
then striped to form a RAID 0 array at the upper level of the hierarchy. The collective result is a
RAID 10 array. The figure below demonstrates a RAID 10 comprised of two RAID 1 arrays at the
lower level of the hierarchy – arrays A and B. These two arrays in turn are striped using 4 stripes
(comprised of the strips 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B etc.) to form a RAID 0 at the upper level of the hierarchy.
The result is a RAID 10.
Advantage:
RAID 10 ensures that if one of the disks in any parity group
fails, its contents can be extracted using the information on the remaining functioning disks in its
parity group. Thus it offers better data redundancy than the simple RAID types such as RAID 1,
3, and 5. Also, a RAID 10 array can improve the throughput of read operations by allowing reads
to be performed concurrently on multiple disks in the set.
RAID Rebuild
When a RAID array enters into a degraded mode, it is advisable to rebuild the
array and return it to its original configuration (in terms of the number and state of working
disks) to ensure against operation in degraded mode.
SATA
Acronym for “
Serial ATA
”. A hard disk drive interface standard developed to enhance
connectivity and speed over the IDE, or Parallel ATA disk interface. Current generation SATAII
supports speeds up to 300MB/S.
Server Message Block (SMB)
a network protocol mainly applied to share files, printers, serial
ports, and miscellaneous communications between nodes on a network. It also provides an
authenticated Inter-process communication mechanism. SMB and its successor, CIFS, are the
native network protocol used by the Microsoft Windows family, and is also used by Apple MacOS
X and is available for virtually every UNIX and Linux operating system.
Span
Spanning or Concatenation of disks is a method for combining multiple physical disk drives
into a single virtual disk, although it is not one of the numbered RAID levels. It provides no data
redundancy; as the name implies, disks are merely concatenated together, end to beginning, so they
appear to be a single large disk. This mode is sometimes called JBOD, or “Just a Bunch Of Disks”
Stripe
A stripe is a logical space that spans across multiple hard disks with each constituent hard
disk contributing equal strips (or chunks) of space to the stripe.
Stripe Set
A stripe set is a set of stripes that spans across multiple hard disks. In the figure below,
the displayed stripe set has 4 stripes, with strip number 1 comprised of the purple strips 1A, 1B
and 1C. Stripe number 2 is comprised of the green strips 2A, 2B and 2C etc.
Stripe Size
This is the size of the strips that constitute each stripe. This term is a misnomer –
though prevalent – since it should appropriately be called strip size or chunk size.
TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol)
A pair of communications protocols
that implement the protocol stack on which the Internet and most commercial networks run. TCP
is a peer-to-peer connection oriented protocol that guarantees the delivery of data packets in
the correct sequence between two peers. IP is the protocol that defines and governs addressing,
fragmentation, reassembly and time-to-live parameters for packets.
D-Glossary