Chapter 7 Alarm Handling 105
Chapter 7 Alarm Handling
This chapter describes the handling of alarms, as well as the preventive maintenance of the system during system
daily operation.
The maintenance personnel must have adequate knowledge about the power system.
18. Note
The maintenance must be conducted under the guidance of related safety regulations.
Only the trained personnel with adequate knowledge about the power system can maintain the inner part of the subrack.
7.1 Handling Alarms
The monitoring module alarms are classified in four types: critical alarm, major alarm, observation and no alarm.
Critical alarm, major alarm: these two types of alarms have strong impacts on the system performance. Whenever
these alarms are generated, users are supposed to handle them immediately. The alarm indicators will be on and
audible indication will be given.
Observation: when this type of alarm is raised, the system maintains normal output for a while. If the alarm occurs
during watch time, it should be handled immediately. If the alarm occurs during non- watch- time, handle it during
watch time. The alarm indicators will be on when observation alarm occurs.
No alarm: if alarms are set as ‘no alarm’ by the users, when these alarms occur, no visible or audible indication will be
generated and the system works normally.
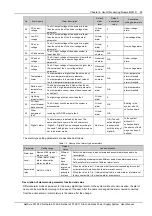
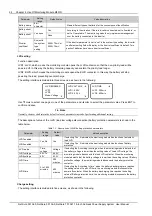
The handling methods of normal alarms are given in Table 6-1.
Table 1.1 System setting parameter description
No.
Alarm
Handling method
1
Mains Failure
If the failure does not last long, the battery will power the load. If the cause is unknown or the failure
lasts too long, a diesel generator is needed. Before using the generator’s power, it is suggested to run
the generator 5 minutes to stabilize the power output
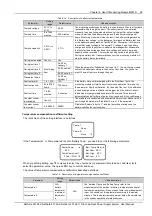
2
AC Voltage High
Check if the AC Over-voltage point is too low. Reset the value if too low
A mild over-voltage does not affect the system operation. However, the rectifier will stop operation when
the mains voltage is more than 305V. Therefore, if the power supply is constantly over-voltage, the
mains power network should be improved
3
AC Voltage Low
Check if the AC Uder- voltage point is too high. Reset the value if too high
When the mains voltage is lower than 176V, the output power of the rectifiers will be derated. If the
power supply is constantly under-voltage, the main power network should be improved
4
DC Volt High
Check the system DC output voltage and value of “Over” set through the monitoring module. If the set
value is improper, correct it.
Find out the rectifier that has caused the alarm.
First of all, ensure that the batteries can operate normally. Then switch off the AC input of all rectifiers.
Power on the rectifiers one by one. If the over-voltage protection is triggered when a certain rectifier is
powered on, that rectifier is the faulty one. Replace the fault recitfier
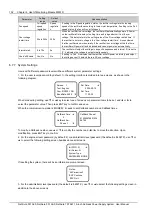
5
DC Volt Low
1. Check the system DC output voltage and value of “Under” set through the monitoring module. If the
set value is improper, correct it
2. If the alarm is caused by mains failure,check if certain loads can be disconnected to prolong the
operation of the whole system
3. If the alarm is due to rectifier fault, find out the faulty rectifier and replace it
4. Compare the total load current with the rectifier current, and the former should not be bigger than the
later at FC voltage, otherwise partial loads must be disconnected to ensure the safe operation of the
whole system. Add several rectifiers to make the total rectifier current bigger than 120% of the total load
current. In addition, there must be at least 1 rectifier for redundancy standby
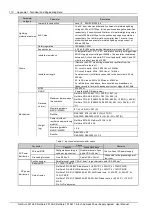
6
Load Fuse
Alarm/ Batt Fuse
Alarm
Check if the MCB of the route is switched off.If the MCB is open, find out the fault and remove it.
Otherwise, the alarm loop is faulty. Please contact Emerson
7
LVD2
1. Check if there is mains failure, or the battery voltage is lower than the “BLVD” value, or the battery
discharge time is more than the “BLVD Time”
2. The battery is disconnected from the system manually
NetSure 501 A50, NetSure 501 AA0, NetSure 701 A51 19-Inch Subrack Power Supply System User Manual