5
User Manual
MN032006EN
Effective December 2017
415U Condor-long-range
wireless I/O and gateway
EATON
www.eaton.com
Powering from the SUP+ and SUP– terminals
The 415U-2 will operate from a 15–30 Vdc supply (nominal 24 Vdc)
connected to the SUP+ and SUP– terminals. The power supply
must be able to supply enough current to operate the device, to
power all of the I/O circuits 415, and to power the device’s radio
transmitter when it is sending data. A 24 Vdc 2.5 A power supply
such as ELPRO PSG60E or PS-DINAC-24DC-OK is suitable for all
configurations, including configurations requiring battery charging
and expansion I/O.
If you need to use a supply with a lower power rating; or if you
need to power additional equipment in your installation; use these
guidelines to determine your required power supply current. Add
the relevant elements from
Table 2
to determine your power supply
current requirement. Remember you also need to add current for
any other equipment being powered from the same power supply,
including relays, loop isolators, indicators, etc.
Table 2. Power supply current requirements
Supply voltage
17 Vdc
24 Vdc
30 Vdc
Base operating current
180 mA
140 mA
100 mA
Radio transmit current
10W FSK
2100 mA
1300 mA
1100 mA
5W FSK
1000 mA
650 mA
500 mA
4W QAM
1800 mA
1200 mA
950 mA
Discrete I/O (per active input or output)
11 mA
7 mA
5 mA
Analog inputs and outputs
(per 20 mA loop)
55 mA
38 mA
30 mA
Connecting a back-up battery to the BAT+ and
GND terminals
The 415U-2 provides an internal battery charger for Sealed Lead
Acid (SLA) batteries. You can connect a 13.8 V SLA battery to the
BAT+ and GND terminals to provide a backup power source if the
main supply fails. While the main supply is present, the battery will
charge at up to 0.5 A rate until the battery voltage reaches 14.3 V.
The battery charger will then maintain a float charge on the battery
at this voltage. To fully charge the SLA battery, the main supply must
be at least 17 Vdc.
When you connect a backup battery, you need to provide sufficient
power to support the additional charge current required when the
battery is discharged (when it is recovering from an extended power
interruption).
Table 3
shows the
additional
current from your power
supply to support battery charging.
Table 3. Additional current to support battery charging
Supply voltage (
V
sup
)
Current required (
I
sup
)
17 Vdc
600 mA
24 Vdc
450 mA
30 Vdc
350 mA
Formula
0
Powering expansion I/O modules
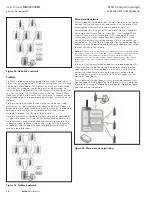
The 415U-2 allows connection of 115S Series modules to the RS-485
port to provide expanded I/O capacity. You can use the “+” and
“–“ connections on the 415U-2 to provide up to 500 mA supply for
expansion I/O modules. If you have a back-up SLA battery connected
to the 415U-2, then this connection will also be powered from the
back-up supply, so that the expansion I/O modules receive the
backup power as well as the main module.
ETHERNET
USB
RS232
SUPPLY
+
-
GND BAT SUP SUP
+
B
A
-
+
115S-xx
115S-xx
RS-485
B
A
B
A
B
A
-
+
-
+
Figure 7. Expansion I/O power and RS
-
485
When the module is being powered from the main supply (SUP+
and SUP– terminals), you need to provide sufficient power to
support the additional current required by the expansion I/O
modules.
Table 4
shows the
additional
current from your power
supply to support expansion I/O connection.
Table 4. Additional supply current to support expansion I/O
Expansion
I/O
current
(
I
exp
)
Current required (
I
sup
)
Supply voltage
17 Vdc
24 Vdc
30 Vdc
Base operating current 115S
120 mA
130 mA
90 mA
75 mA
Discrete inputs
(per active input)
13 mA
14 mA
10 mA
8 mA
Discrete outputs
(per active output)
25 mA
27 mA
20 mA
16 mA
Analog inputs and outputs
(per 20 mA loop)
50 mA
55 mA
38 mA
30 mA
Formula
0
Powering the module directly from the BAT+ and
GND terminals
In some situations you may want to power the module directly
from a 13.8 Vdc supply. This could be because this voltage supply is
already available at an installation; because the power requirements
for 115S modules are more than can be supplied by the “+” and “–“
expansion I/O connections; or because the installation cannot meet
thermal requirements when being powered from the SUP inputs
(refer to “Thermal” on
page 3
).
Use
Table 5
to determine the device’s current requirements at
13.8 Vdc. Remember you also need to add current for any other
equipment being powered from the same power supply, including
relays, indicators, and any additional 115S modules.
Table 5. Current requirements
Supply current at 13.8 Vdc
Base operating current
180 mA
Radio transmit current
10W FSK
2500 mA
5W FSK
1300 mA
4W QAM
2100 mA
Discrete I/O (per active input or output)
10 mA
Analog inputs and outputs (per 20 mA loop)
50 mA