- 4 -
2. Working Principle
Different matter has different but special absorbance wavelength point. Also, when at
the fixed wavelength point, the absorbance has some relation to the substance
’
s
(Always transparent Solution) concentration and its thickness. The relation can be
concluded as the following Formula which is called Lambert-Beer Law.
T= I/I
o
A=KCL= -log I/I
o
A
Absorbance
C
Concentration of the Solution
K
Absorbance Coefficient of the Solution
L
The length of the Solution in the light path
I The intensity of the light focused on the A/D after it permeate the
solution to be measured.
I
o
The intensity of the light focused on the A/D after it permeate the
Solution.
Note
: When test, the solvent is usually taken as the Reference Solution and its
Transmittance is considered as 100%T. While the Transmittance of the sample to
be tested is a relative value which is got comparing to that of the Reference.
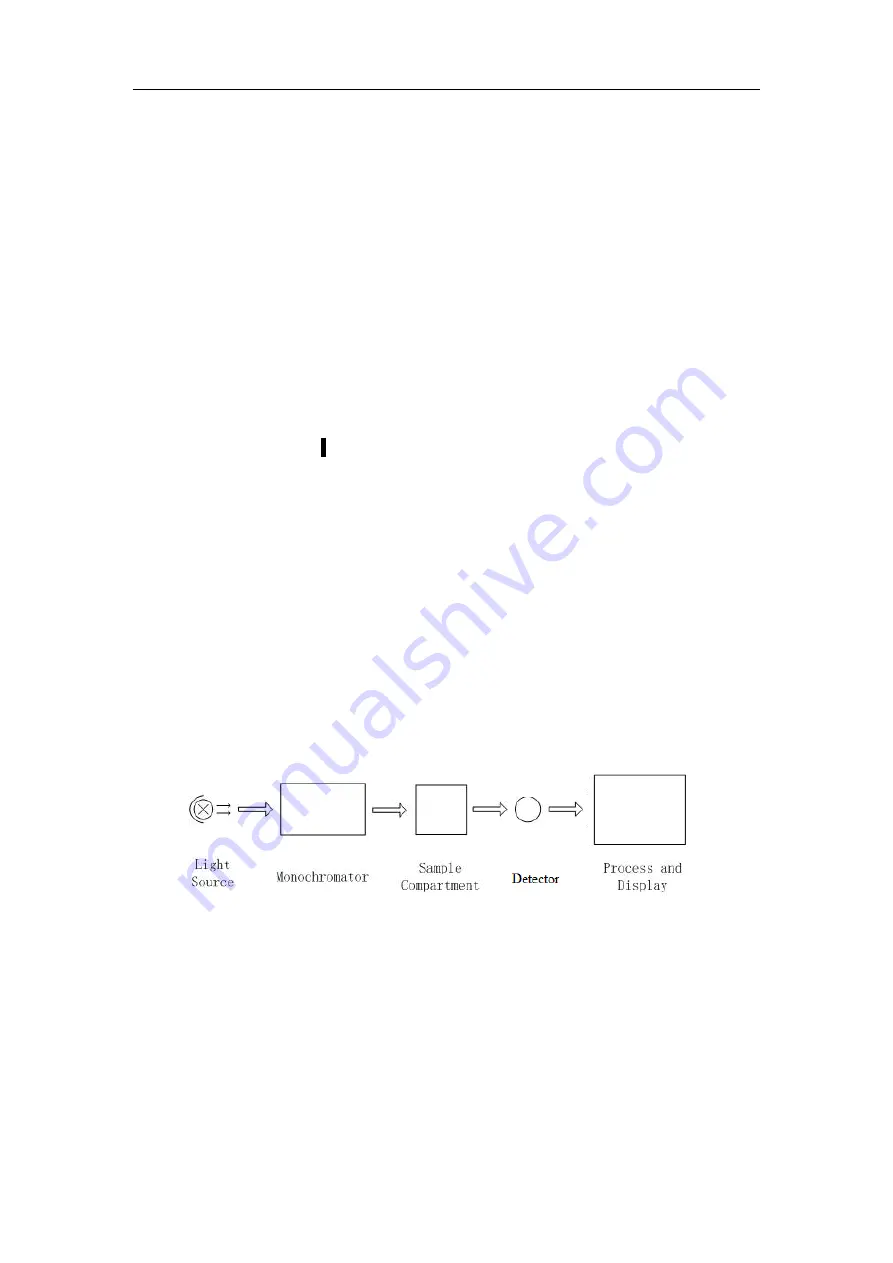
3. Structure
The spectrophotometer consists of five parts:
1) Halogen or deuterium lamps to supply the light;
2) A Monochromator to isolate the wavelength of interest and eliminate the unwanted
second order radiation;
3) A sample compartment to accommodate the sample solution;
4) Detector to receive the transmitted light and convert it to an electrical signal; and
5) A digital display to indicate absorbance or transmittance. The block diagram (Fig
2-4) below illustrates the relationship between these parts.
Fig 2-4 Block diagram for the Spectrophotometer
In your spectrophotometer, light from the lamp is focused on the entrance slit of the
monochromator where the collimating mirror directs the beam onto the grating. The
grating disperses the light beam to produce the spectrum, a portion of which is focused
on the exit slit of the monochromator by a collimating mirror. From here the beam is
passed to a sample compartment through one of the filters, which helps to eliminate
unwanted second order radiation from the diffraction grating. Upon leaving the
sample compartment, the beam is passed to the silicon photodiode detector and
causes the detector to produce an electrical signal that is displayed on the digital
display.








































