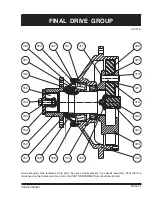
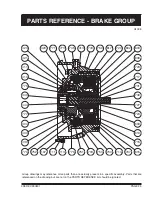
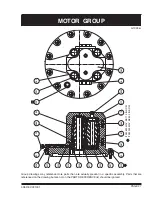
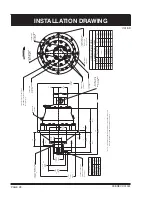
PAGE 13
FAILURE
PROBABLE CAUSE
TROUBLE SHOOTING
CONTINUED
Brake will not hold load.
Brake vibrates or chatters when lowering load.
a)
Hydraulic system back pressure not per SPECIFICATIONS.
Refer to procedure described in TROUBLE SHOOTING -
HYDRAULIC SYSTEM PRESSURE AND PLANEMATIC
TORQUE to verify system back pressure at motor.
b)
Brake piston release oil being trapped by hydraulic system
control valve. Control valve spool must open motor ports to
reservoir when in the neutral position. Refer to
RECOMMENDATIONS - HYDRAULIC CONTROL VALVE.
c)
Worn brake and/or divider plates. Inspect brake plates and
divider plates for wear as described in SERVICE
INSTRUCTIONS - DISASSEMBLY OF BRAKE ASSEMBLY.
d)
Damaged brake and/or divider plates. Plate discolouration
and distortion will occur if plates overheat due to insufficient
circulation flow. Required brake circulation flow is listed in
SPECIFICATIONS. Plate abrasion damage will occur if
contamination is present in hydraulic fluid.
e)
Damaged over-running clutch. Inspect sprag clutch,
connecting shaft and motor drive shaft as described in
SERVICE INSTRUCTIONS - DISASSEMBLY OF BRAKE
ASSEMBLY.
f)
Damaged brake springs. Measure brake springs as
described in SERVICE INSTRUCTIONS - DISASSEMBLY
OF BRAKE ASSEMBLY. Verify springs are straight and
length is as indicated.
g)
Seized brake piston. Brake piston could be seized by
hydraulic fluid contamination, scored brake housing bore or
damaged piston O-rings.
a)
Inadequate hydraulic flow. Refer to procedure described in
TROUBLE SHOOTING - HYDRAULIC SYSTEM VOLUME
AND PLANEMATIC SPEED to verify supply.
b)
Inadequate hydraulic control. System control valve must
have good metering characteristics.
c)
Foamy hydraulic fluid. Foam will occur if air is mixed with
hydraulic oil.
d)
Worn brake and/or divider plates. Inspect brake plates and
divider plates for wear as described in SERVICE
INSTRUCTIONS - DISASSEMBLY OF BRAKE ASSEMBLY.
e)
Damaged brake plates and/or divider plates. Plate
discolouration and distortion will occur if plates overheat
due to insufficient circulation flow. Required brake circulation
flow is listed in SPECIFICATIONS. Plate abrasion damage
will occur if contamination is present in hydraulic fluid.
f)
Damaged over-running clutch. Inspect sprag clutch, connecting
shaft and motor drive shaft as described in SERVICE
INSTRUCTIONS - DISASSEMBLY OF BRAKE ASSEMBLY.
a)
Damaged O-ring. Static O-rings seal between the end
cover and final housing, final housing and brake housing ,
brake housing and motor adaptor. Another O-ring seals
brake release pressure between the motor adaptor and
brake housing. A failed O-ring will result in oil leakage at
that particular area.
b)
Worn or damaged output shaft seal. Excessive circulation
return line back pressure can damage this seal. Refer to
procedure described in TROUBLE SHOOTING - HYDRAULIC
SYSTEM PRESSURE AND PLANEMATIC TORQUE to
measure back pressure. Back pressure must never exceed
the allowable circulation return line back pressure listed in
SPECIFICATIONS. Back pressure will be higher at start-up
and during cold weather when oil viscosity is greater.
Oil leaks.
338 REV.990801
Refer to the SERVICE INSTRUCTIONS if it becomes necessary to disassemble the Planematic drive.