Chapter 5 Parameters
|
VFD-B-P Series
5-90
Revision April 2009, SW V1.00
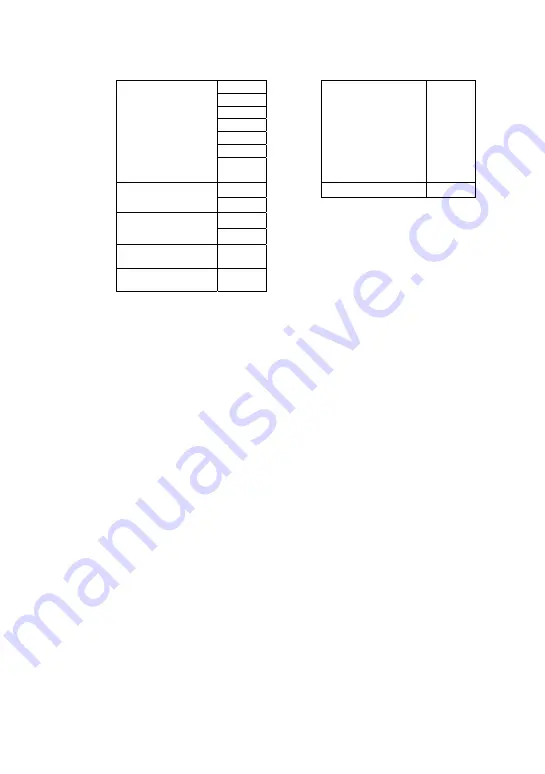
RTU mode:
Command message:
Response message:
Address 01H
Address 01H
Function 10H
Function 10H
05H
05H
Starting data
address
00H
Starting data address
00H
00H’
00H
Number of data
(count by word)
02H
Number of data
(count by word)
02H
Number of data
(count by byte)
04
CRC Check Low
41H
13H
CRC Check High
04H
The first data
content
88H
0FH
The second data
content
A0H
CRC Check Low
‘4D’
CRC Check High
‘D9’
3.4 Check sum
ASCII mode:
LRC (Longitudinal Redundancy Check) is calculated by summing up, module 256, the values of
the bytes from address to data content then calculating the hexadecimal representation of the 2’s-
complement negation of the sum.
For example, from above table, the calculation should be 01H+03H+21H+02H+00H+02H=29H.
The 2’s complement negation of 29H is D7H.
RTU mode:
CRC (Cyclical Redundancy Check) is calculated by the following steps:
Step 1:
Load a 16-bit register (called CRC register) with FFFFH.
Step 2:
Exclusive OR the first 8-bit byte of the command message with the low order byte of the
16-bit CRC register, putting the result in the CRC register.
Step 3:
Examine the LSB of CRC register.
Step 4:
If the LSB of CRC register is 0, shift the CRC register one bit to the right with MSB zero
filling, then repeat step 3. If the LSB of CRC register is 1, shift the CRC register one bit to the right
with MSB zero filling, Exclusive OR the CRC register with the polynomial value A001H, then repeat
step 3.
Step 5:
Repeat step 3 and 4 until eight shifts have been performed. When this is done, a complete
8-bit byte will have been processed.
Step 6:
Repeat step 2 to 5 for the next 8-bit byte of the command message. Continue doing this
until all bytes have been processed. The final contents of the CRC register are the CRC value.
When transmitting the CRC value in the message, the upper and lower bytes of the CRC value
must be swapped, i.e. the lower order byte will be transmitted first.
















































