Precautions
Service Manual
1-5
1.3 ESD Precautions
Certain semiconductor devices can be easily damaged by static electricity . Such components are commonly called
“Electrostatically Sensitive (ES) Devices”, or ESDs. Examples of typical ESDs are: integrated circuits, some field
effect transistors, and semiconductor “chip” components.
The techniques outlined below should be followed to help reduce the incidence of component damage caused by
static electricity.
Caution >>Be sure no power is applied to the chassis or circuit, and observe all other safety precautions.
1. Immediately before handling a semiconductor component or semiconductor-equipped assembly , drain of f any
electrostatic charge on your body by touching a known earth ground. Alternatively, employ a commercially avail -
able wrist strap device, which should be removed for your personal safety reasons prior to applying power to the
unit under test.
2. After removing an electrical assembly equipped with ESDs, place the assembly on a conductive surface, such as
aluminum or copper foil, or conductive foam, to prevent electrostatic charge buildup in the vicinity of the assem -
bly.
3. Use only a grounded tip soldering iron to solder or desolder ESDs.
4. Use only an “anti-static” solder removal device. Some solder removal devices not classified as “anti-static” can
generate electrical charges sufficient to damage ESDs.
5. Do not use Freon-propelled chemicals. When sprayed, these can generate electrical charges sufficient to dam-
age ESDs.
6. Do not remove a replacement ESD from its protective packaging until immediately before installing it. Most
replacement ESDs are packaged with all leads shorted together by conductive foam, aluminum foil, or a compa -
rable conductive material.
7. Immediately before removing the protective shorting material from the leads of a replacement ESD, touch the pro-
tective material to the chassis or circuit assembly into which the device will be installed.
8. Maintain continuous electrical contact between the ESD and the assembly into which it will be installed, until com-
pletely plugged or soldered into the circuit.
9. Minimize bodily motions when handling unpackaged replacement ESDs. Normal motions, such as the brushing
together of clothing fabric and lifting one’ s foot from a carpeted floor , can generate static electricity suf ficient to
damage an ESD.
1. Exercise caution when replacing a super capacitor or Lithium battery . There could be a danger of explosion and
subsequent operator injury and/or equipment damage if incorrectly installed.
2. Be sure to replace the battery with the same or equivalent type recommended by the manufacturer.
3. Super capacitor or Lithium batteries contain toxic substances and should not be opened, crushed, or burned for
disposal.
4. Dispose of used batteries according to the manufacture’ s instructions.
1.4 Super Capacitor or Lithium Battery Precautions
Summary of Contents for 1815 Mono Laser
Page 1: ...Dell 1815dn Service Manual 27 Mar 2006 ...
Page 28: ...Service Manual System Outline 4 10 ...
Page 126: ...Exploded View Parts List Service Manual 8 3 8 2 Cover Ass y 0 1 2 2 3 2 1 2 2 3 4 5 5 1 5 2 6 ...
Page 127: ...Service Manual Exploded View Parts List 8 4 8 3 Middle Cover Ass y 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 6 ...
Page 129: ...Service Manual Exploded View Parts List 8 6 8 5 Rear Cover Ass y 0 1 2 3 7 4 5 6 8 ...
Page 131: ...Service Manual Exploded View Parts List 8 8 8 7 Fuser Drive Ass y 0 1 2 3 5 5 6 7 8 9 4 ...
Page 132: ...Exploded View Parts List Service Manual 8 9 8 8 Main Drive Ass y 0 2 4 1 3 5 6 8 7 6 7 3 ...
Page 136: ...Exploded View Parts List Service Manual 8 13 8 12 OPE Unit 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ...
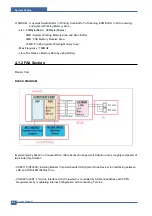
Page 149: ...Block Diagram Service Manual 9 1 9 9 9 Block Diagram ...
Page 150: ...Connection Diagram Service Manual 10 1 10 10 10 Connection Diagram ...