Certificate Authority (optional)
The components of the SDDC require SSL certificates for secure operation. During deployment, self-signed certificates are used for each
of the deployed components. These certificates can be replaced with certificates that are signed by an internal enterprise CA or by a third-
party commercial CA.
If you plan to replace the self-signed certificates, the CA must be able to sign a Certificate Signing Request (CSR) and return the signed
certificate. All endpoints within the enterprise must also trust the root CA of the CA.
If you plan to deploy vRealize Automation, a Certificate Authority is required, and the certificates are required during installation.
Physical network requirements
Before deploying Cloud Foundation, configure the physical network to enable the following features:
•
VLAN Tagging (802.1Q)
•
Jumbo frames
– A minimum MTU value of 1600 is required, however it is recommended that you set the MTU to 9000.
Network pools
Cloud Foundation uses a construct that is called a network pool to automatically configure VM kernel ports for vSAN, NFS, and vMotion.
Cloud Foundation uses an Internet Protocol Address Management (IPAM) solution to automate the IP configuration of VM kernel ports for
vMotion, vSAN, and NFS (depending on the storage type being used).
When a server is added to the inventory of Cloud Foundation, it goes through a process called host commissioning. During this process, the
hosts are associated with an existing network pool. When the host is provisioned during the create VI workload domain, add cluster, or add
host workflow, it automatically configures the VMkernel ports and allocates IP addresses for vMotion, vSAN, and NFS from the network
pool the host was associated with.
You can expand the included IP address range of a network pool at any time, however you cannot modify the other network information.
Ensure that you have defined each subnet in the network pool to account for current and future growth in your environment.
VLANs and IP subnets
Network traffic types within Cloud Foundation are isolated from each other by using VLANs. Before deploying your SDDC, you must
allocate VLAN IDs and IP subnets for each required traffic type. Configure the VLAN IDs and IP subnets in your network to pass traffic
through your network devices. Before you start the Cloud Foundation deployment, verify that the allocated network information is
configured and does not conflict with pre-existing services before starting your Cloud Foundation deployment.
The number and size of the subnets that are required for a deployment depends on:
•
The number of workload domains that are created
•
The number of clusters defined
•
The optional components that are installed
The following table lists the basic allocation of VLANs and IP subnets for a sample deployment. Use this sample to define the VLANs and IP
subnets in your environment.
34
Cloud Foundation and SDDC design considerations
Summary of Contents for PowerEdge MX7000
Page 1: ...Dell EMC VMware Cloud Foundation for PowerEdge MX7000 Deployment Guide ...
Page 8: ...Figure 1 Cloud Foundation deployment workflow 8 Overview ...
Page 27: ...Figure 19 Dual PowerEdge MX7000 enclosure configuration Physical layout 27 ...
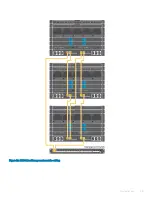
Page 29: ...Figure 20 MX9002m Management module cabling Physical layout 29 ...
Page 30: ...Figure 21 Connectivity between FSE modules and FEM modules 30 Physical layout ...
Page 31: ...Figure 22 Uplinks to customer network environment Physical layout 31 ...
Page 42: ...Figure 25 MX9002m Management Module cabling 42 Networking requirements ...
Page 43: ...Figure 26 Connectivity between FSE modules and FEM modules Networking requirements 43 ...
Page 44: ...Figure 27 Uplinks to customer network environment 44 Networking requirements ...