©2015 Cradlepoint. All Rights Reserved.
|
+1.855.813.3385
|
cradlepoint.com
63
User Manual
/
AER3100/AER3150
DNS SERVERS
DNS, or Domain Name System, is a naming system that translates between domain names (www.cradlepoint.
com, for example) and Internet IP addresses (206.207.82.197). A DNS server acts as an Internet phone book,
translating between names that make sense to people and the more complex numerical identifiers. The DNS
page for the device has these distinct functions:
•
DNS Settings
: By default your router is set to automatically acquire DNS servers through your Internet
provider (Automatic). DNS Settings allows you to specify DNS servers of your choosing instead (Static).
•
Split DNS
: Enable or disable the redirecting of specified domains to alternate DNS servers.
•
Dynamic DNS Configuration
: Allows you to host a server (Web, FTP, etc.) using a domain name that you
have purchased (www.example.com) with your dynamically assigned IP address.
•
Known Hosts Configuration
: Allows you to map a name (printer, scanner, laptop, etc.) to an IP address of a
device on the network.
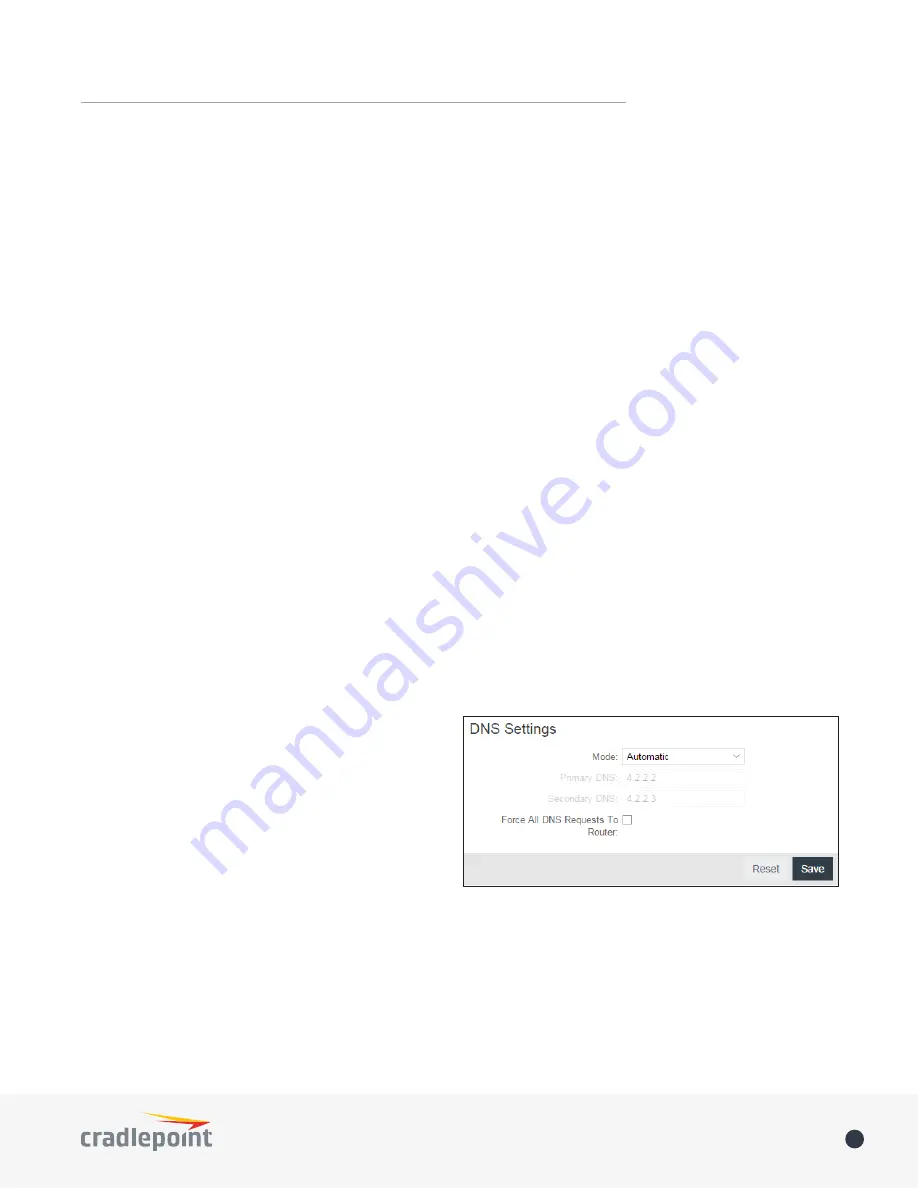
DNS Settings
You have the option to choose specific DNS servers for your network instead of using the DNS servers
assigned by your Internet provider. The default DNS servers are usually adequate. You may want to assign DNS
servers if the default DNS servers are performing poorly, if you want WiFi clients to access DNS servers that
you use for customized addressing, or if you have a local DNS server on your network.
Mode
: Automatic or Static (default: Automatic).
Switching to “Static” enables you to set specific DNS
servers in the
Primary DNS
and
Secondary DNS
fields.
Primary DNS
and
Secondary DNS
: If you choose
to specify your DNS servers, then enter the IP
addresses of the servers you want as your primary
and secondary DNS servers in these fields. The DNS
server settings will be pre-populated with public DNS
server IP addresses. You can override the IP address
with any other DNS server IP address of your choice.
For example, Google Public DNS servers have the IP addresses 8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4 while 4.2.2.2 and 4.2.2.3 are
servers from Level 3 Communications.
Force All DNS Requests To Router
: Enabling this will redirect all DNS requests from LAN clients to the router’s
DNS server. This will allow the router even more control over IP addresses even when clients have their own
DNS servers statically set.
Split DNS
Split DNS allows you create two zones for the same domain, one to be used by the internal network, the
other used by the external network. Split DNS directs internal hosts to an internal domain name server for
until multiple packets have already bypassed a rule. Application sets require an active license to exist on the
device for them to function.
DSCP (DiffServ)
: Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) is the successor to TOS (Type of Service). Use
this field to select traffic based on the DSCP header in each IP packet. This field is sometimes set by latency
sensitive equipment such as VoIP phones. This setting is optional.
DSCP Negate
: When checked this rule will match on any packet that does not match the DSCP field.
Click
Finish
to save this rule.
















































