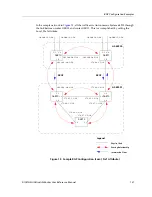
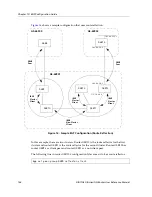
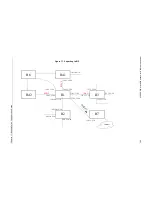
DIGITAL GIGAswitch/Router User Reference Manual
145
Route Import and Export Policy Overview
Aggregates and Generates
Route aggregation is a method of generating a more general route, given the presence of a
specific route. It is used, for example, at an autonomous system border to generate a route
to a network to be advertised via BGP given the presence of one or more subnets of that
network learned via OSPF. The routing process does not perform any aggregation unless
explicitly requested.
Route aggregation is also used by regional and national networks to reduce the amount of
routing information passed around. With careful allocation of network addresses to
clients, regional networks can just announce one route to regional networks instead of
hundreds.
Aggregate routes are not actually used for packet forwarding by the originator of the
aggregate route, but only by the receiver (if it wishes). Instead of requiring a route-peer to
know about individual subnets which would increase the size of its routing table, the peer
is only informed about an aggregate-route which contains all the subnets.
Like export policies, aggregate-routes can have up to three components:
•
Aggregate-Destination
•
Aggregate-Source
•
Route-Filter
Aggregate-Destination
This component specifies the aggregate/summarized route. It also specifies the attributes
associated with the aggregate route. The preference to be associated with an aggregate
route can be specified using this component.
Aggregate-Source
This component specifies the source of the routes contributing to an
aggregate/summarized route. It can also specify the preference to be associated with the
contributing routes from this source. This preference can be overridden by explicitly
specifying a preference with the route-filter.