6.1.2 DMZ
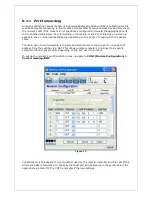
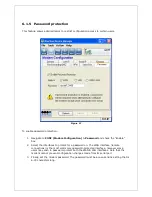
This feature, when enabled, instructs the modem to forward all incoming traffic to a single IP
destination on the LAN. An exception will be made for traffic coming on the ports designated
by the port-forwarding rules (this would be ports 9000, 23, and 777 in Figure 13). This
exception can be overridden by checking the “DMZ overrides all forwarded ports below”
checkbox.
DMZ is ideal in situations where there is already a server on the LAN that handles port-
forwarding, as it avoids having to re-program all the port-forwarding rules into the modem. It
is also practical when the user does not know which ports his local device listens on, and just
wants everything to work with minimal configuration.
DMZ can be enabled at
CONF (Modem Configuration) > Port Forwarding/DMZ
.
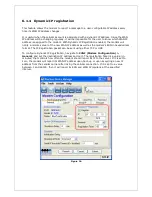
6.1.3 IP Pass-through
When this feature is enabled, the modem will disable NAT and assign its WAN IP address to
the attached host. The modem will remain reachable though its reserved TCP and UDP ports.
To enable IP pass-through, navigate to
CONF (Modem Configuration) > LAN IP
and select
the data interface to perform pass-through on, then check the “Enable IP Pass-through”
checkbox.
If IP pass-through is enabled, then port-forwarding and DMZ should be disabled.
If the host is attached to the modem via an Ethernet cable, then the host must
have DHCP enabled (i.e., it should be perform automatic IP negotiation instead of
using a pre-defined static IP).
Figure 14
Figure 15