- 52 -
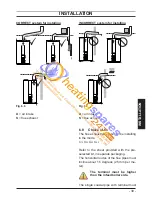
INST
ALLA
TION
COMMISSIONING
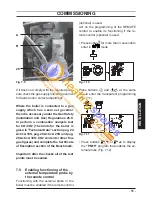
Fig. 7.2
24
22
Gradually open stopcock at the fi lling point
•
connection to the c.h. system until water is
heard to fl ow; do not open fully.
Open each radiator air vent starting at
•
the lowest point of the system and close
it only when clear water, free of bubbles,
fl ows out.
Purge the air from the pump by unscrew-
•
ing the pump plug 24 ( Fig. 7.2 ); release
the pump shaft by turning in the direction
indicated by the arrow on the information
plate.
Replace the pump plug.
•
Continue fi lling the system. The actual
•
reading should ideally be 1,3 bar and not
less than 0,3 bar.
Close all air release valves on the c.h.
•
system.
Inspect the boiler and the system for wa-
•
ter tightness and remedy any leaks dis-
covered.
Cold fl ush the system to remove any loose
•
particles and any system debris before
starting the boiler for the fi rst time
The fl ushing procedure must be in line
with BS7593:2006 Treatment of Water in
d.h.w. c.h. Systems.
When the installation and second fi ll-
ing are completed turn on the c.h. sys-
tem and run it until the temperature has
reached the boiler operating tempera-
ture. The system must then be immedi-
ately fl ushed through.
This procedure must be repeated twice
more.
During this operation a c.h. fl ushing de-
tergent must be used in the quantities
as specifi ed by the appropriate manu-
facturer, whose function it is to dissolve
any foreign matter which may be in the
system.
INHIBITION (Primary Heating Circuit)
On the fi nal refi lling of the heating system it
is important to ensure the system water is
treated with a suitable scale and corrosion
inhibitor in accordance with the manufactur-
ers instructions.
Condensate pipe and traps
7.5
The full length of the condensate pipe
should be check for leaks.
Before running the boiler, ensure that the
built in condensate trap and any other trap
in the drain system is correctly fi lled with
water.
Fill the built in condensate trap
by removing the fl ue elbow and
pouring a cupful of water into
the fl ue outlet ( Fig. 7.3 ).