Product overview
EL37x2
18
Version: 3.5
3.5
Basic function principles
The analog EL3702/ EL3742 input terminal enables measurement of two voltages/currents, which can be
displayed with a resolution of 16 bit (65535 steps).
The oversampling feature enables the terminal to sample analog input values several times during each bus
cycle on each channel.
Oversampling
A conventional analog input terminal samples one analog input value ("sample") during each bus cycle and
transfers it to the higher-level control system during the next fieldbus cycle. The EL37x2 samples the voltage
several times between two fieldbus communication cycles configurable and at equidistant intervals. A 16-bit
packet of x analog measured values is transferred to the higher-level control system during the next fieldbus
communication cycle. This procedure is referred to as oversampling.
Distributed Clock
Oversampling requires a clock generator in the terminal that triggers the individual data sampling events.
The local clock in the terminal, referred to as distributed clock, is used for this purpose.
The distributed clock represents a local clock in the EtherCAT slave controller (ESC) with the following
characteristics:
• Unit
1 ns.
• Zero point
1.1.2000 00:00.
• Size
64 bit
(sufficient for the next 584 years); however, some EtherCAT slaves only offer 32-bit
support, i.e. the variable overflows after approx. 4.2 seconds.
• The EtherCAT master automatically synchronizes the local clock with the master clock in the EtherCAT
bus with a precision of < 100 ns.
The EL37x2 only offers 32-bit support.
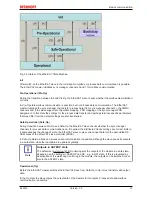
Sample:
The fieldbus/EtherCAT master is operated with a cycle time of 1 ms to match the higher-level PLC cycle time
of 1 ms, for example. This means that every 1 ms an EtherCAT frame is sent to collect the process data from
the EL37x2. The local terminal clock therefore triggers an interrupt in the ESC every 1 ms (1 kHz), in order to
make the process data available in time for collection by the EtherCAT frame. This first interrupt is called
SYNC1.
The EL37x2 may be set to oversampling n = 10 in the TwinCAT System Manager. This causes the ESC to
generate a second interrupt in the terminal with an n-times higher frequency, in this case 10 kHz or 100 µs
period. This interrupt is called SYNC0. At each SYNC0 signal the analog-to-digital converter (ADC) starts a
data sampling event, and the sampled analog values are sequentially stored in a buffer.
Note
Determining the input voltages/input currents
Both input voltages / input currents (channels 1 and 2) are always sampled simultaneously.
This is ensured by the ADC type that is triggered by the SYNC0 pulse. No other operation
mode is possible.
Generation of the SYNC0 pulse from the local synchronized clock within the distributed clock network
ensures that the analog values are sampled at highly equidistant intervals with the period of the SYNC1
pulse.
The maximum oversampling factor depends on the memory size of the used ESC and in the KKYY0000
version of the EL37x2, it is n = 100.
Summary of Contents for EL3702
Page 2: ......
Page 6: ...Table of contents EL37x2 6 Version 3 5...
Page 83: ...Commissioning EL37x2 83 Version 3 5 Fig 92 Incorrect driver settings for the Ethernet port...
Page 142: ...Commissioning EL37x2 142 Version 3 5 Fig 184 Process data tab SM0 EL37x2...
Page 143: ...Commissioning EL37x2 143 Version 3 5 Fig 185 Process data tab SM1 EL37x2...