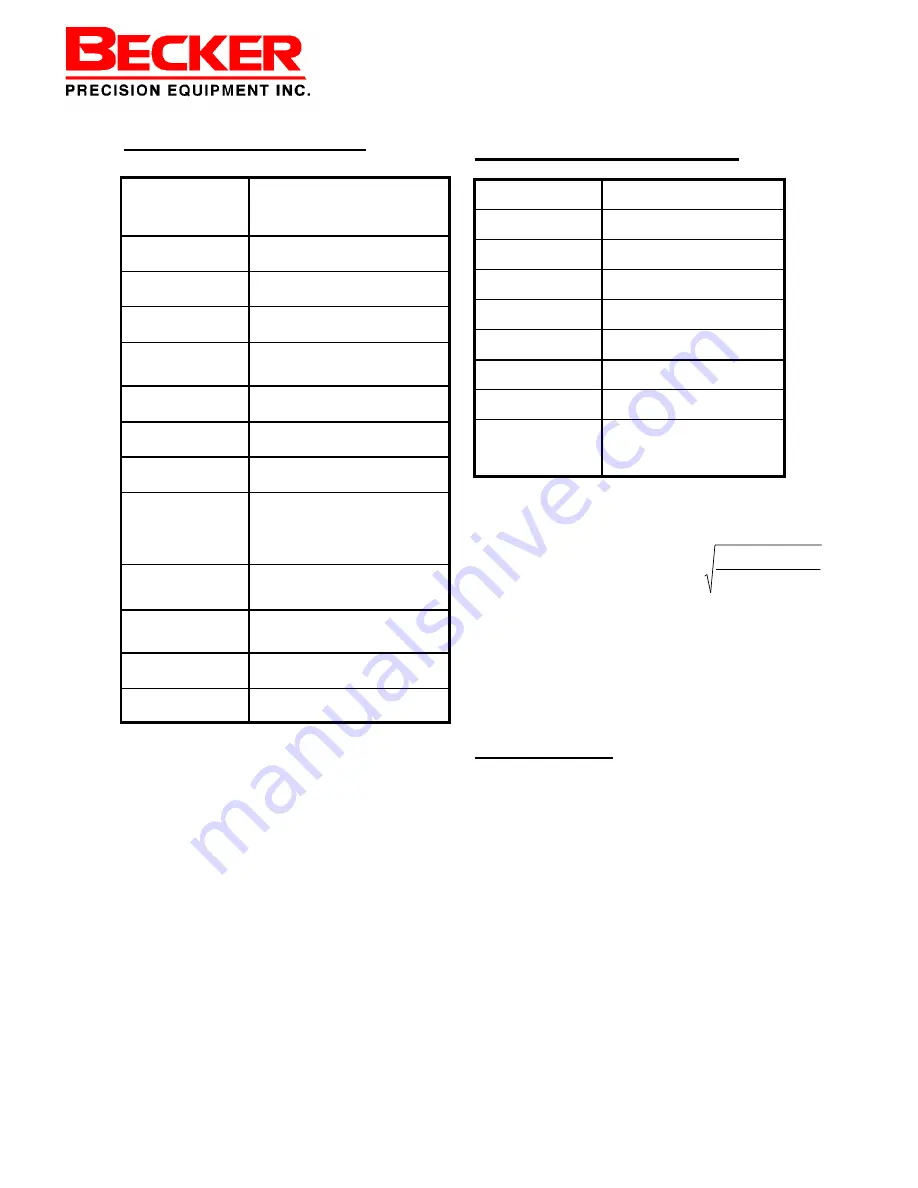
Maximum Supply Regulator Capacity
Q
=
Min. Supply Regulators Capacity
(scfh)
G
=
Specific Gravity of Gas
T
=
460 + Operative Temperature (
°
F)
Cv =
Flow Factor
P
1
=
Supply Pressure to Positioner (psig)
Accessories
•
Atmospheric Bleed Control (
AB Control
)
:
maintains minimum pressure differential
across the cylinder. The AB Control is re-
quired in order to provide the necessary
output to operate the control valve under all
design conditions.
•
NBV No Bleed valve – same function as
DPS, no adjustments or tubing required.
Works up to 150 psig power gas.
•
DPS Series Non-Bleed Sensor:
achieves
non-bleeding conditions in either full open
or full closed positions. Selection based
upon power gas pressure and discharge
gas pressure.
Input Signal:
Standard:
3-15 psi or 6-30 psi.
Adjustable:
Zero is adjustable from 2-
30 psig, span is adjustable from 5-24
Output Signal:
Pneumatic pressure as required by the
actuator up to full supply pressure.
Loss of Signal:
Reverse Acting:
Open on loss of signal.
Direct Acting:
Close on loss of signal.
Connections:
All Ports: ¼” N.P.T.
Action:
Direct and Reverse Acting:
. Field-
reversible
Performance:
Resolution:
0.4%*
Hysteresis:
.6%*
Flow Capacity:
C
V
= 1.5
Steady State
Consumption:
Near Zero
Power Gas Require-
ment:
Use clean, dry filtered (100 micron)
gas.
Discharging to Atmosphere:
150 psig maximum.
Operative Temperature
Limits:
-20 to 160
°
F
(-28 to 70
°
C).
Housing:
Meets NEMA 3 classification (weather
tight).
Installation Orienta-
tion:
Vertical or horizontal position allow-
able.
Approximate Weight:
15 pounds.
External Parts:
Anodized 2024 Aluminum
Internal Parts:
316 Stainless Steel and 2024 Ano-
dized Aluminum
Feedback Lever:
316 Stainless Steel
Range Spring:
Plated Music Wire
Diaphragms:
Buna-N with Nylon Reinforcement
Seats and O-Rings:
Buna-N
Tubing:
316 Stainless Steel
Fittings:
316 Stainless Steel
Gauges:
2 ½” Dial Liquid filled Brass Con-
nection with Stainless Steel Case.
(Stainless Steel connection op-
HPP-5 Positioner
Specifications
Technical Specifications
Materials of Construction
HPP-5
4
September 1999
Q
= 312.86 x
P
1
x C
V
x
)
(
460
1
+
×
T
G
* Resolution and repeatability figures reflect a
positioner that is adjusted with a minimum dead-
band to reduce bleed gas. If the deadband is
eliminated (slightly increasing the bleed gas),
resolution and repeatability will improve.






















