45
45
E
Example No. 10
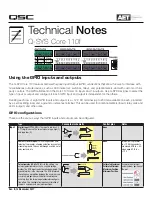
Put the relevant read/write head into ground state:
Both read/write heads can be independently set to the ground state.
Host:
1.)
Process subaddresses of the output buffer:
BIS C-60_2 Identification System:
2.)
Go to ground state;
Process subaddresses of the input buffer:
3.)
Process subaddresses of the output buffer:
4.)
Process subaddresses of the input buffer:
00
Hex
/07
Hex
Set GR-Bit
00
Hex
/07
Hex
Reset BB-Bit
00
Hex
/07
Hex
Reset GR-Bit
00
Hex
/07
Hex
Set BB-Bit
Function Description
Examples for protocol sequence
C60_2-028_823024_0401-e.p65
46
46
E
Read times from
data carrier to
processor in
static mode
(parametering:
2nd byte, bit 5 = 0)
The indicated times apply after the data carrier has been recognized. If the data carrier is not
yet recognized, an additional 45 ms for building the required energy field until the data carrier is
recognized must be added.
For double read and compare:
Data carrier with 32 byte blocksData carrier with 64 byte blocks
No. of bytesRead time [ms
]
No. of bytesRead time [ms
]
from 0 to 31
110
from 0 to 63
220
for each additional
32 bytes add
120
for each additional
64 bytes add
230
from 0 to 255
= 950
from 0 to 2047
= 7350
Including readback and compare:
Data carrier with 32 byte blocksData carrier with 64 byte blocks
No. of bytes
Write time [ms]
No. of bytes
Write time [ms]
from 0 to 31
110 + n * 10
from 0 to 63
220 + n * 10
for 32 bytes or more
y * 120 + n * 10
for 64 bytes or more
y * 230 + n * 10
n = number of contiguous bytes to write
y = number of blocks to be processed
Example: 17 bytes from address 187 have to be written. Data carrier with 32 bytes per block.
The blocks 5 and 6 will be processed since the start address 187 is in block 5 and the end
address 203 in block 6.
t = 2 * 120 + 17 * 10 = 410 ms
Write times from
processor to data
carrier in static
mode
(parametering:
2nd byte, bit 5 = 0)
Read/Write Times
☞
All manuals and user guides at all-guides.com