18
4.3.3 Compressed-air system (option)
)
Prior to each application, proper function of the display
instruments and control valves must be checked!
Purpose of compressed-air system:
a) Medicaments can be applied to the nasopharynx:
• The pump for the compressed-air system switches on
after the compressed-air handle has been removed from
its holder.
• Handle is mounted on a sprayer. The top of the
compressed-air handle locks in place in the ring of the
sprayer bottle.
• Available sprayers:
- with straight spraying tube for normal liquid
medicaments
- with twin tube and adjustable angular jet for oily
medicaments.
)
If a sprayer is used with medication the instructions of the
medication manufacturers have to be observed.
)
Do not use the sprayer for the storage of medication!
)
Caution to be paid to avoid injury when introducing
sprayer jet!
Please note, in case the ventilation opening is blocked or
the sprayer head is immersed in fluids (e.g. blood, secretion,
etc.) a negative pressure could occur and the fluid could
flow back into the bottle.
In this case the medicine sprayer, sprayer head, flexible
nozzle as well as the hose piece for the medicine sprayer
must be reprocessed as described in chapter 5.0 cleaning.
• Pull the release lever.
ª
The medicament sprayer is supplied with air and the
medicament in the sprayer bottle is atomized.
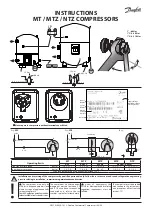
• The amount of compressed air is adjusted with
the control knob (
3
, fig 17) in conjunction with the
compressed air gauge (
2
, fig 17).
• After use, the medicament sprayer is again inserted in its
holder, the bar is pressed, the handle is removed from
the sprayer and again inserted in its support.
ª
Compressed-air system is again switched off.
)
For hygienic reasons, the spraying tubes are to be
exchanged following each application or with each
patient.
Fig. 17. Compressed-air system
Sprayer suspension
Compressed-air display
Compressed-air control
Support for automatic photoelectric barrier control
Compressed-air handle
4.0 Operation
1
2
3
4
5
1
2
3
4
5