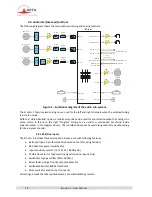
S
COOPY
+ S - User Manual
17
2.2.5.
G722 coding
Application: commentaries, coordination. Low latency.
This mono coding algorithm at a 64 kbit/s bit rate is a reference for commentaries, and features a 50-
7000 Hz bandwidth.
It is available, ISDN, IP networks (wired or mobile).
For ISDN, three synchronisation modes are possible:
"Statistical recovery" byte synchronisation method (alias SRT);
H221 synchronisation; in this case, 1.6 kbit/s from the compressed data are used for this;
H221 synchronisation and H242 protocol.
H221 synchronisation is highly recommended when possible, as it features higher reliability and faster
recovery time, while degradation (because of the bit rate used for framing) is minimal.
H242 protocol, the most flexible mode, is recommended by the ITU-T, and is included in J52. However,
the mode with H221 synchronisation but without H242 protocol can be useful for compatibility with old
generation codecs which did not use this protocol.
No specific synchronisation is required for the IP mode.
2.2.6.
TDAC coding
Application: commentaries, mono music via ISDN with only one B channel.
The S
COOPY
+ S can also include the TDAC algorithm. TDAC is for Time Domain Aliasing Cancellation; this
is a transform coding based on an MDCT (
Modified Discrete Cosine Transform
), encoding a 15 kHz
bandwidth mono signal at a 64 kbit/s bit rate.
TDAC is available as an option, only for the ISDN mode.
2.2.7.
4SB ADPCM coding
Application: commentaries, mono or stereo music. Low latency.
4SB ADPCM operates either in mono at a 128 kbit/s rate, or in stereo at 256 kbit/s, for a 15 kHz
bandwidth. It features a very low latency which makes it very interesting for live duplex transmission. It
also has the advantage to be very little sensitive to tandem coding.
4SB ADPCM is available for ISDN (Mono only); wired or mobile IP. However it is not recommended for
mobile networks, because it requires a high bit rate and it is highly sensitive to packet losses, which can
be frequent on such networks.