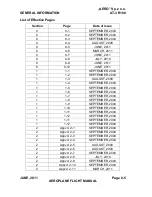
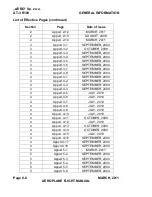
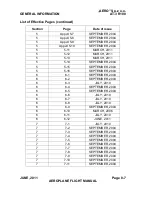
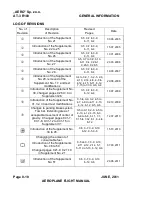
Reviews:
No comments
Related manuals for AT-3 R100

BSS501
Brand: Makita Pages: 60

25304
Brand: Eastwood Pages: 3

21320
Brand: Eastwood Pages: 8

21302
Brand: Eastwood Pages: 12

11797
Brand: Eastwood Pages: 4

CONTOUR SCT
Brand: Eastwood Pages: 12

HTR-1
Brand: parktool Pages: 4

GB703SH-5
Brand: Gage Bilt Pages: 24

GB703SRV
Brand: Gage Bilt Pages: 24

GB703SHAVT
Brand: Gage Bilt Pages: 24

6516-M125
Brand: Bison Pages: 44

Pocket-Hole Jig 7pce
Brand: Triton Pages: 20

61018
Brand: Max Pages: 87

MagJig 95
Brand: Magswitch Pages: 2

05PE
Brand: Atlas Copco Pages: 24

Clic
Brand: Caillau Pages: 14

5411074164935
Brand: Work Men Pages: 48

337334-2007
Brand: Parkside Pages: 96