l&M V 6584 R16 sec1
©ASCO Valve, Inc. 50 Hanover Road, Florham Park, New Jersey 07932
www.ascovalve.com
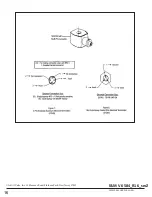
NOTE:
Connector housing may be rotated in 90° increments from
position shown for alternate positioning of cable entry.
Check DIN connector terminal block for electrical markings. Then
make electrical hookup to terminal block according to markings
on it. Snap terminal block into connector cover and install center
screw.
Position connector gasket on solenoid and install plug connector.
Torque center screw to 5±1 in-lbs [0,6±1,1 Nm].
6.
5.
NOTE:
Alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) sole-
noids are built differently and cannot be converted from one to the
other by changing the coil.
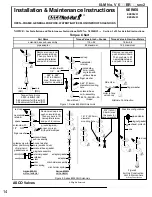
Installation of Solenoid
Solenoids may be assembled as a complete unit. Tightening is
accomplished by means ofa hex flange at the base of the solenoid.
Installation of Panel Mounted Solenoid
(See Figures 1 and 2)
Install solenoid base sub-assembly through customer panel.
8202H panel mounted solenoids include a retainer to adapt the
solenoid base sub-assembly to the customer panel. (See Figure 2)
Position finger washer on opposite side of panel over solenoid
base sub-assembly.
Replace solenoid, nameplate/retainer and red cap.
Make electrical hookup, see Wiring section.
Disassemble solenoid following instruction under
Solenoid
Replacement
then proceed.
2.
3.
4.
1.
5.
Solenoid Temperature
Standard solenoids are designed for continuous duty service. When
the solenoid is energized for a long period, the solenoid becomes
hot and can be touched by hand only for an instant. This is a safe
operating temperature.
MAINTENANCE
A WARNING: To prevent the possibility of death,
serious injury or property damage, turnoff electrical
power, depressurize solenoid operator and/or valve,
and vent fluid to a safe area before servicing.
Cleaning
All solenoid operators and valves should be cleaned
periodically. The time between cleaning will vary depend-
ing on medium and service conditions. In general, if the
voltage to the solenoid is correct, sluggish valve operation,
excessive noise or leakage will indicate that cleaning is
required. Clean strainer or filter when cleaning the valve.
Preventive Maintenance
•
Keep the medium flowing through the solenoid opera
-
tor or valve. as free from dirt and foreign· material as
possible.
• Periodic exercise of the valve should be considered if
ambient or fluid conditions are such that corrosion, elas
-
tomer degradation, fluid contamination build up, or other
conditions that could impede solenoid valve shifting are
possible. The actual frequency of exercise necessary will
depend on specific operating conditions. A successful op
-
erating history is the best indication of a proper interval
between exercise cycles.
• Depending on the medium and service conditions,
periodic inspection of internal valve parts for damage or
excessive wear is recommended. Thoroughly clean all
parts. Replace any worn or damaged parts.
Causes of Improper Operation
• Faulty Control Circuit:
Check the electrical system by
energizing the solenoid. A metallic click signifies that
the solenoid is operating. Absence of the click indicates
loss of power supply. Check for loose or blown fuses,
open-circuited or grounded solenoid, broken leadwires or
splice connections.
• Burned-Out Solenoid:
Check for open-circuited so-
lenoid. Replace if necessary. Check supply voltage; it
must be the same as specified on nameplate/retainer and
marked on the solenoid. Check ambient temperature and
check that the core is not jammed.
• Low Voltage:
Check voltage across the solenoid leads.
Voltage must be at least 85% of rated voltage.
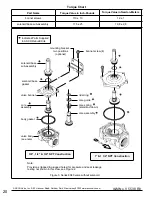
Solenoid Replacement
1. Disconnect conduit, coil leads, and grounding wire.
NOTE:
Any optional parts attached to the old solenoid must
be reinstalled on the new solenoid. For 3-way construction,
piping or tubing must be removed from pipe adapter.
2. Disassemble solenoids with optional features as follows:
• Spade or Screw Terminals
Remove terminal connections, grounding screw, ground-
ing wire, and terminal block (screw terminal type only).
NOTE:
For screw terminals, the socket head screw holding
the terminal block serves as a grounding screw
.
• Junction Box
Remove conduit and socket head screw (use 5/32” hex key
wrench) from center of junction box. Disconnect junction
box from solenoid.
• DIN Plug Connector
Remove center screw from DIN plug connector. Disconnect
DIN plug connector from adapter. Remove socket head
screw (use 5/32” hex key wrench), DIN terminal adapter,
and gasket from solenoid.
1
2
Summary of Contents for E-STOP09
Page 28: ...28...