Model DT33x-0700
4-Wire DC I/V Dual Transmitter w/USB
Acromag, Inc. Tel: 248-295-0880
- 23 -
http://www.acromag.com
- 23 -
https://www.acromag.com
Calibration (Optional)
…
If your output acts erratic or appears imprecise,
you may need to repeat the channel input or
output calibration, being very careful to connect
and select the correct channel, take accurate
measurements, and adjust correct signal levels.
For current outputs, if you are measuring a
voltage across an output load resistor, make sure
that you use the exact load resistance when
calculating the load current being measured.
Also, for rescaled input ranges, make sure that
you still have adequate input span (12-bit or
better), as an input span set too-tight will have
diminished resolution and magnified error.
Note:
Input calibration from the factory has all
sub-ranges of a nominal input range along an
input terminal path calibrated automatically by
extrapolating from the calibration of the major
range for that path to save time (see
Specifications Table 1 and note the ranges that
share the same divider and gain setting). One
exception is ±1mA of the DT236 where its gain
doubles requiring it be calibrated separately
from ±20mA. However, you still have the option
of calibrating a specific sub-range independent of
its major range to increase precision if required,
but make sure you always calibrate the smaller
input range after its major range to prevent the
subsequent re-calibration of a range from
stepping on the calibration of a smaller sub-
range.
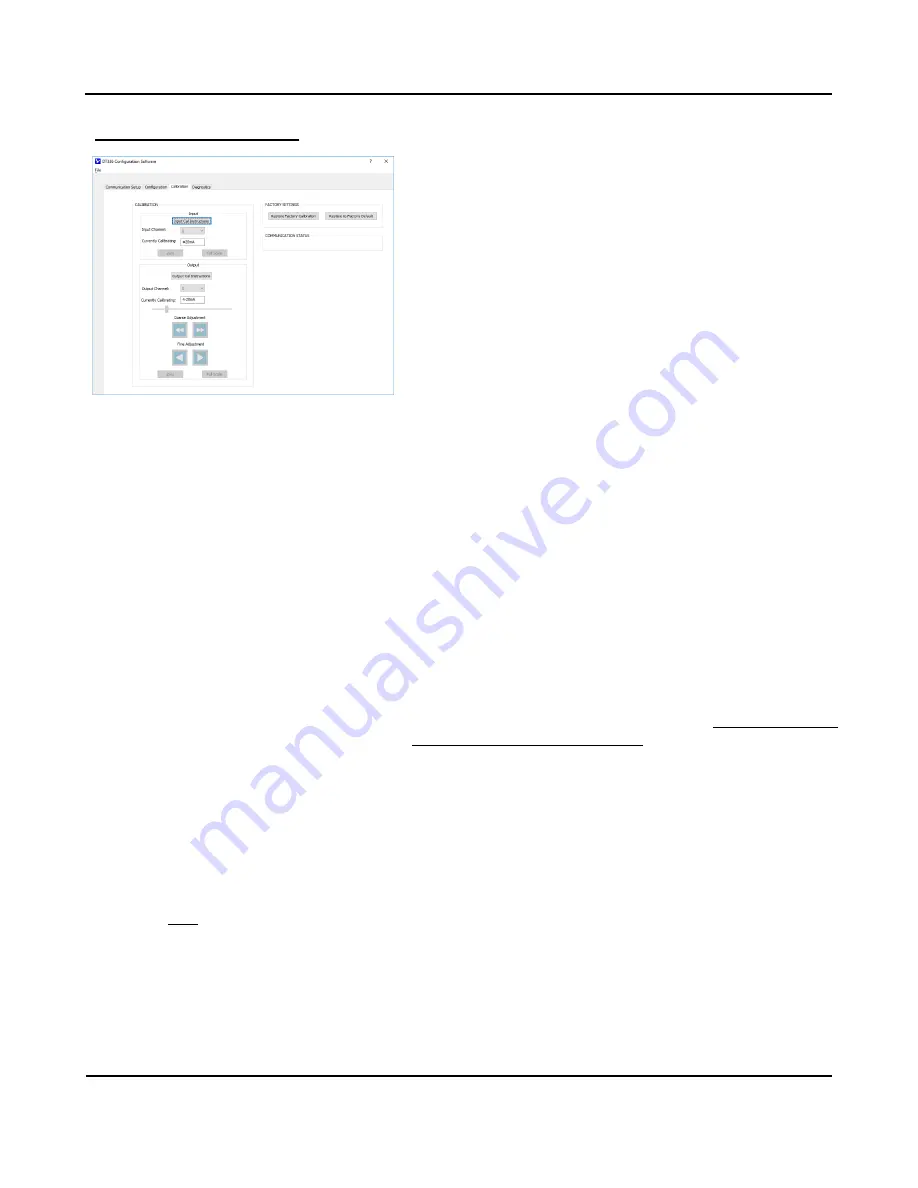
CALIBRATION
–
Each Output Separately
Wire your output monitor to the correct terminal, voltage or current,
for the channel output you wish to calibrate. Set your nominal output
Range to calibrate
on the “
Configuration
” page
and make sure you
write your selection to the unit by clicking
[Send I/O Config].
On the calibration page, select the Output Channel to calibrate, 1 or
2. Then click
[Output Cal Instructions]
to begin output calibration by
enabling the Output adjustment controls and [Zero] and [Full-Scale]
buttons.
Use the Output Course and Fine Adjustment controls to drive the
output to its precise nominal output zero (i.e. 0mA, 4.000mA, -10V, -
5V, or 0V, depending on the nominal output range setting) as
indicated by your output meter. Measure this output level very
accurately, or output performance will be degraded. At the precise
output range zero, click Output
[Zero]
of Calibration - Output to
calibrate the output zero.
Use the Output Course and Fine Adjustment controls to drive the
output to its precise nominal output full-scale (i.e. 20.000mA, 5V, or
10V, depending on the nominal output range setting). Measure this
output level very accurately, or output performance will be degraded.
At the precise output range full-scale, click Output
[Full-Scale]
of
Calibration - Output to calibrate the output full-scale level.
CALIBRATION
–
FACTORY SETTINGS
You can use the
[Restore Factory Calibration]
button to restore the
transmitter
’s original factory calibration if you think you made an
error during recalibration, have degraded its performance, or the I/O
channel appears erratic.
You can use the
[Restore to Factory Default]
button to return the
unit to its original factory configuration settings. This option does not
restore calibration, only configuration. Alternately, this button can be
used as a sanitation tool to restore the unit to its initial configuration
when decommissioning a module.
CALIBRATION
–
COMMUNICATION STATUS
This field displays calibration status messages like “No Error”,
“Transfer Error”, and “Timeout Error” during calibration. If you
encounter a Transfer or Timeout Error, your calibration did not take
effect and you may have to repeat the calibration process.






























