Chapter 13 Spanning Tree Protocol
XMG1930 Series User’s Guide
158
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
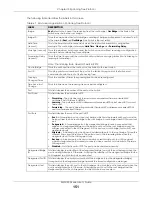
Table 71 Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol > Status: MSTP
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Click
Configuration
to specify which STP mode you want to activate. Click
MSTP
to edit MSTP
settings on the Switch.
CST
This section describes the Common Spanning Tree settings.
Bridge
Root
refers to the base of the spanning tree (the root bridge).
Our Bridge
is this switch. This
Switch may also be the root bridge.
Bridge ID
This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of bridge priority plus MAC address. This ID
is the same for
Root
and
Our Bridge
if the Switch is the root switch.
Hello Time
(second)
This is the time interval (in seconds) at which the root switch transmits a configuration
message. The root bridge determines
Hello Time
,
Max Age
and
Forwarding Delay
.
Max Age (second)
This is the maximum time (in seconds) the Switch can wait without receiving a configuration
message before attempting to reconfigure.
Forwarding Delay
(second)
This is the time (in seconds) the root switch will wait before changing states (that is, listening to
learning to forwarding).
Cost to Bridge
This is the path cost from the root port on this Switch to the root switch.
Port ID
This is the priority and number of the port on the Switch through which this Switch must
communicate with the root of the Spanning Tree.
Configuration
Name
This field displays the configuration name for this MST region.
Revision Number
This field displays the revision number for this MST region.
Configuration
Digest
A configuration digest is generated from the VLAN-MSTI mapping information.
This field displays the 16-octet signature that is included in an MSTP BPDU. This field displays the
digest when MSTP is activated on the system.
Topology
Changed Times
This is the number of times the spanning tree has been reconfigured.
Time Since Last
Change
This is the time since the spanning tree was last reconfigured.
Instance
These fields display the MSTI to VLAN mapping. In other words, which VLANs run on each
spanning tree instance.
Instance
This field displays the MSTI ID.
VLAN
This field displays which VLANs are mapped to an MSTI.
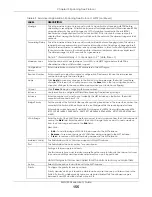
MSTI
Select the MST instance settings you want to view.
Bridge
Root
refers to the base of the MST instance.
Our Bridge
is this switch. This Switch may also be
the root bridge.
Bridge ID
This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of bridge priority plus MAC address. This ID
is the same for
Root
and
Our Bridge
if the Switch is the root switch.
Internal Cost
This is the path cost from the root port in this MST instance to the regional root switch.
Port ID
This is the priority and number of the port on the Switch through which this Switch must
communicate with the root of the MST instance.
Port
This field displays the number of the port on the Switch.
Port State
This field displays the port state in STP.
•
Discarding
– The port does not forward or process received frames or learn MAC
addresses, but still listens for BPDUs.
•
Learning
– The port learns MAC addresses and processes BPDUs, but does not forward
frames yet.
•
Forwarding
– The port is operating normally. It learns MAC addresses, processes BPDUs
and forwards received frames.
Содержание MG1930-30
Страница 19: ...19 PART I User s Guide ...
Страница 46: ...46 PART II Technical Reference ...
Страница 261: ...XMG1930 Series User s Guide 261 Figure 180 Advanced Application LLDP LLDP Local Status LLDP Local Port Status Detail ...
Страница 336: ...XMG1930 Series User s Guide 336 Figure 242 Example Lock Denoting a Secure Connection EXAMPLE ...
Страница 373: ...373 PART III Troubleshooting and Appendices ...