6
5.
Maintenance and Inspection
5.1 Troubleshooting and Corrective Measures
If the pump operation becomes unstable or trouble is caused to its oil discharge during operation, make a
check according to the following procedure.
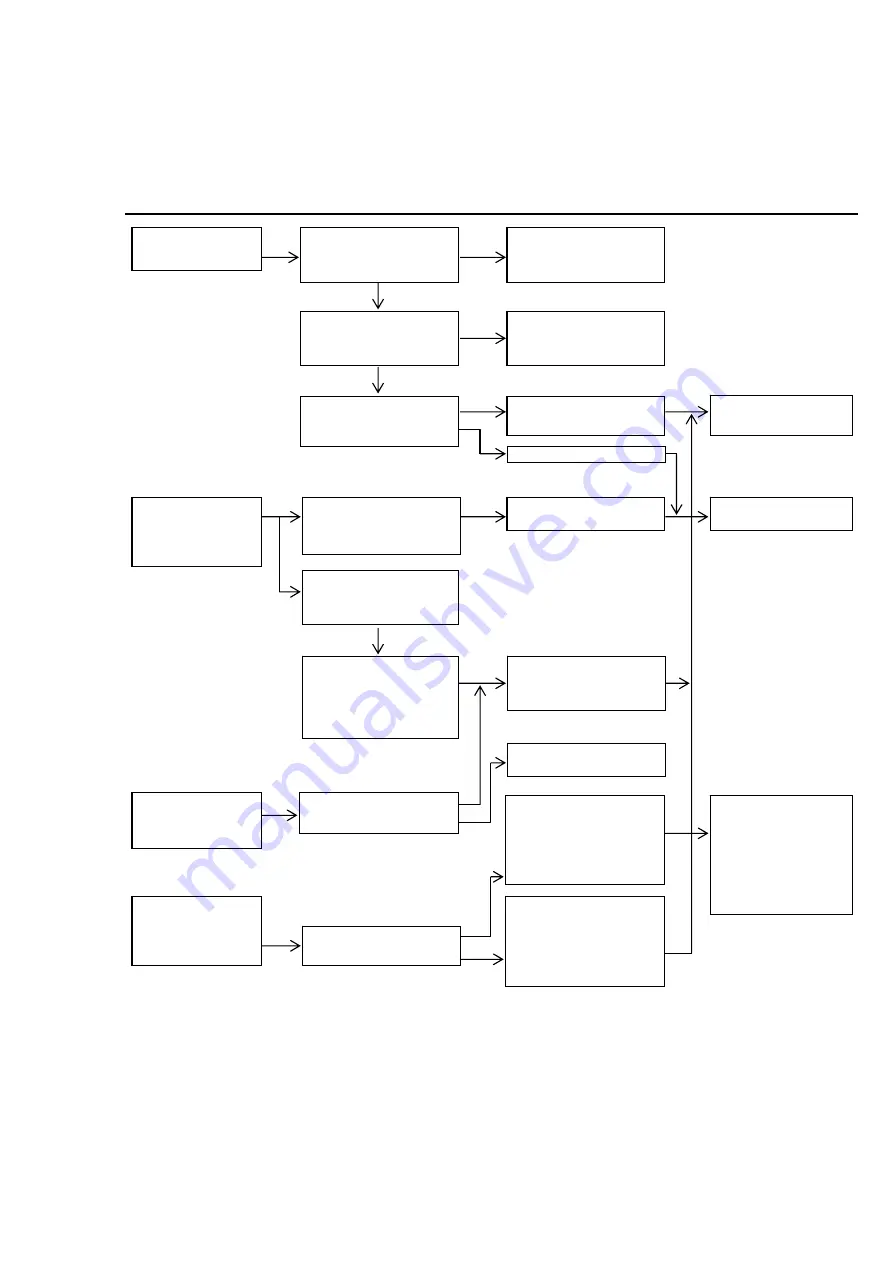
Symptom Cause Contents of inspection and corrective measures
The pump cannot
be operated.
Check if the air
regulator is normally
operated.
Check if the valve on
the outlet on the pump
side is not closed.
Remove the lower pump
and operate the air
motor independently.
Check if the valve in
the course of piping is
not closed.
Clogging occurs in the
connecting hose, pipe,
outlet valve, or gun.
The lower pump is
faulty.
The packing seal of the
air motor is worn away.
Ask for servicing the
lower pump
The pump is
continuously
operated without
stop.
Check if oil does not
leak at the exhaust
port.
Check if there is any
open valve on the
material output side.
The air motor is faulty.
Ask for servicing the
air motor.
When the outlet side is
closed, check if any leak
does not occur on the
pipe, connecting hose or
its connecting portion.
The valve of the lower
pump or the packing is
worn away.
The pump can be
operated but oil is
not fed by pressure.
The pump can be
operated but the
discharge volume is
insufficient.
Check oil is included in
the container.
Check if the supply air
pressure is not lowered.
Check and re-supply, or
replace.
The air supply
volume to the pump
is insufficient.
Replace the air hose
with a thicker one or
check the air
compressor.
check
check
operable
Increase the pressure
up to 0.7 MPa by the air
regulator. At this time,
the oil volume does not
reach the specified level.
The valve seat surface
of the lower pump is
worn away or clogging
is caused by dust or
foreign substances.
NO
YES
YES
NO
YES
NO
inoperable
NO






































