LISA-U2 series - System Integration Manual
UBX-13001118 - R19
Early Production Information
System description
Page 81 of 175
4.
If the data has been exchanged, the slave deactivates
SPI_SRDY
to process the received information. The
master does not need to de-assert
SPI_MRDY
as it controls the
SPI_SCLK
5.
After the preparation, the slave activates again
SPI_SRDY
and wait for
SPI_SCLK
activation. When the clock
is active, all data is transferred without intervention. If there is more data to transfer (flag set in any of the
headers), the process will repeat from step 3
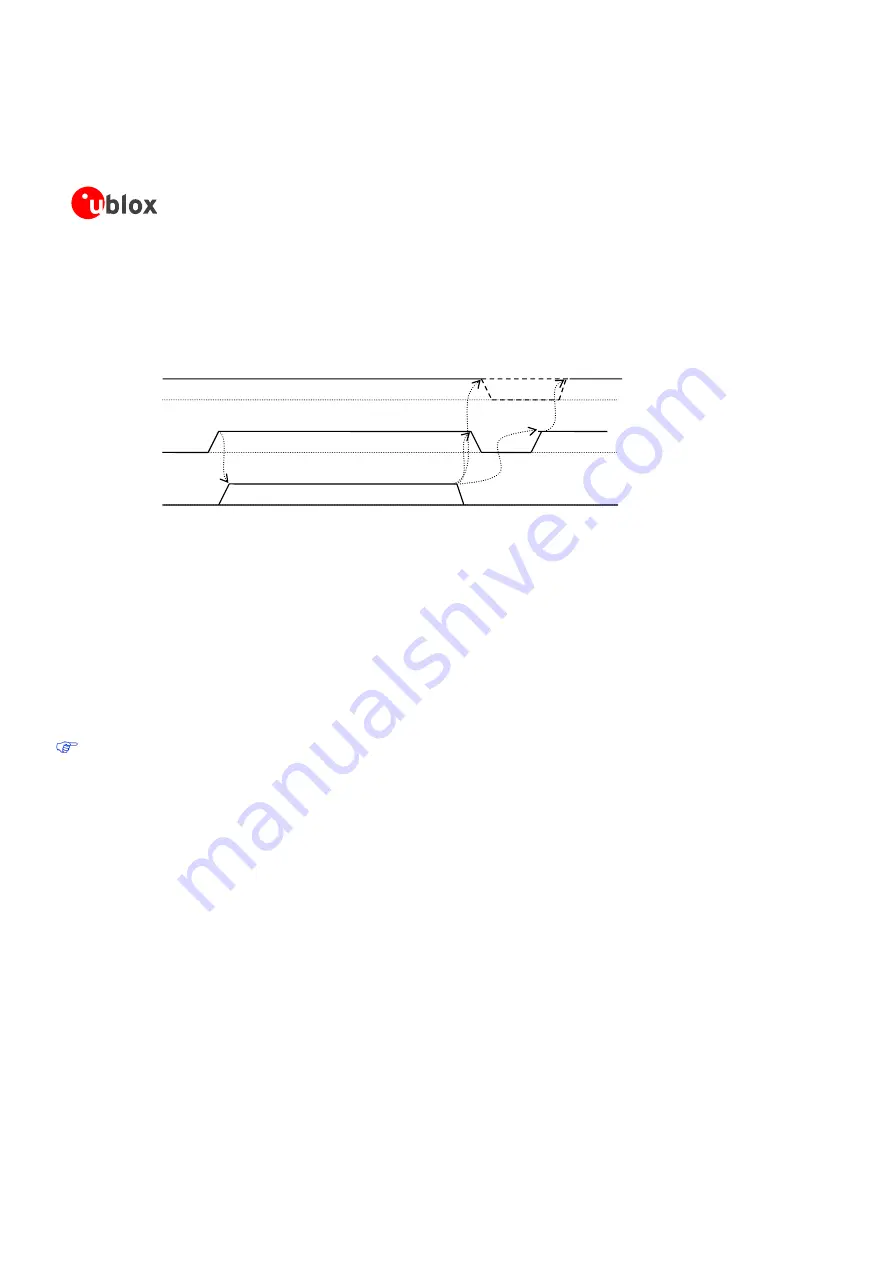
Slave ended transfer
Figure 44: Data transfer terminated and then restarted by LISA-U2 module (slave)
Starting from the state where data transfer is ongoing, the following actions will happen:
1.
In case of the last transfer, the master will lower its
SPI_MRDY
line. After the data-transfer is finished the
line must be low. If the slave has already set its
SPI_SRDY
line, the master must raise its line to initiate the
next transfer (slave-waking-procedure)
2.
If the data has been exchanged, the slave will deactivate
SPI_SRDY
to process the received information. This
is the normal behavior
3.
The slave will indicate the master that is ready to send data by activating
SPI_SRDY
4.
When the master is ready to send, it will signalize this by activating
SPI_MRDY
. This is optional, when
SPI_MRDY
is low before
5.
The slave indicates immediately after a transfer termination that it is ready to start transmission again. In this
case the slave will raise
SPI_SRDY
again. The
SPI_MRDY
line can be either high or low: the master has only
to ensure that the
SPI_SRDY
change will be detected correctly via interrupt
For more details regarding IPC communication protocol, see the
SPI Application Note
1.9.4.4
IPC application circuits
SPI_MOSI
is the data line input for the module since it runs as SPI slave: it must be connected to the data line
output (MOSI) of the application processor that runs as an SPI master.
SPI_MISO
is the data line output for the module since it runs as SPI slave: it must be connected to the data line
input (MISO) of the application processor that runs as an SPI master.
SPI_SCLK
is the clock input for the module since it runs as SPI slave: it must be connected to the clock line
output (SCLK) of the application processor that runs as an SPI master.
SPI_MRDY
is an input for the module able to detect an external interrupt which comes from the SPI master: it
must be connected to a GPIO of the application processor that runs as an SPI master.
SPI_SRDY
is an output for the module that must be connected to a pin of the application processor that runs as
an SPI master able to detect an external interrupt which comes from the module.
Signal integrity of the high speed data lines may be degraded if the PCB layout is not optimal, especially when
the SPI lines are very long: keep routing short and minimize parasitic capacitance to preserve signal integrity. It is
recommended to match the length of SPI signals.
SPI_MRDY
SPI_SRDY
DATA EXCHG
5
2
1
Header
Data
3
4
















































