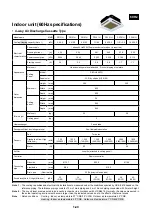
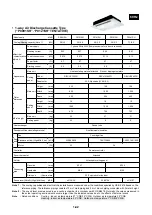
1-28
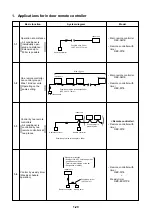
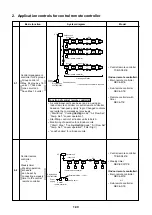
1. Control via indoor remote con-
troller
1-1. Remote Contoller
Individual air-conditioning units can be
controlled remotely (from up to 500 m
away)
1-2. Group Control
One remote controller can control a
maximum of 16 indoor units in group
1-3. Two controlling positions
The units can be controlled from two
locations using two remote controllers
with timer or one remote controller with
timer and one with weekly timer.
1-4. Weekly timer
The units can be run on a weekly
schedule using a “remote controller
with weekly timer”.
2. Control via the central remote
controller
2-1. Central c individual control
The units can be controlled using the
central remote controller and/or indoor
remote controllers.
2-2. Centralized control of 64 groups
A maximum of 1,024 indoor units in 64
different groups can be controlled from
a central location.
2-3. Weekly timer controller
The central remote controller can be
connected to a weekly timer to set a
weekly running schedule.
2-4. Control without indoor remote
controller
The units can be operated from the
central remote controller only, without
the use of indoor remote controllers.
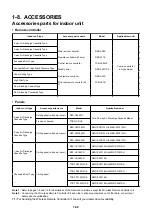
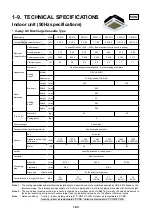
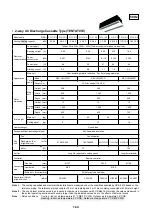
1-7. CONTROLS
Enabling a range of controls to meet various system needs
As the size of the building increases so does the number of air-condition-
ing units required. The multiple air-conditioning system MMS ensures
energy-saving and comfort by allowing a control of multiple units requiring
different loads.
The MMS provides a range of functions to enable an integrated, centralized
control of multiple units. Design an optimal system that best suits the
application and scale of your project.