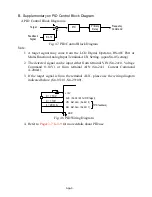
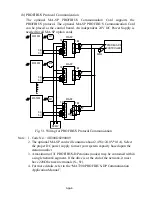
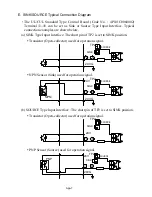
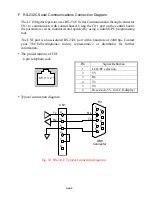
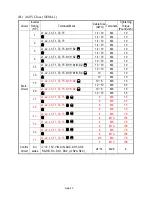
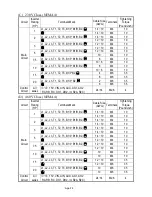
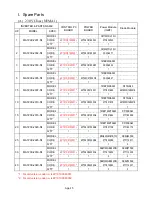
App-1
APPENDIX
A. Adjusting PID Controller
Use the following procedure to activate PID control and then adjust it while
monitoring the response.
1.
Enable PID control. (Sn-64 = 1)
2.
Increase the Proportional gain Bn-17 as far as possible without creating
oscillation.
3.
Decrease the Integral Time Bn-18 as far as possible without creating
oscillation.
4.
Increase the Derivative Time Bn-19 as far as possible without creating
oscillation.
The Proportional, Integral and Derivative control function provides closed-loop
control, or regulation, of a system process variable (pressure, temperature, etc.).
This regulation is accomplished by comparing a feedback signal with a reference
signal, which results in an error signal. The PID control algorithm then performs
calculations, based upon the PID parameter settings (Bn-16 through Bn-20 on Page
3-2
), on this error signal. The result of the PID algorithm is then used as the new
frequency reference, or is added to the existing speed reference.
The PID target value can come from the frequency command (from operator) or a
Multi-Function Analog Input.
Select the PID Control Feedback signal from external terminal AIN for a current
signal (4-20mA DC) or from VIN for a voltage (0-10 VDC).
The Proportional Gain is the value by which the error signal is multiplied to
generate a new PID controller output. A higher setting will result in a system with
quicker response. A lower setting will result in a more stable yet slower system.
The Integral Time is a parameter that determines how fast the PID controller will
seek to eliminate any steady-state error. The smaller the setting, the faster the error
will be eliminated. To eliminate the integral function entirely, set this parameter to
0.0 seconds. A lower setting will result in a more responsive system. A higher
setting will result in a more stable yet slower system.
The Integral Upper Limit parameter will limit the effect that the integrator can have.
It works if the PID controller output is positive or negative. It can also be used to
prevent integrator “wind-up.”
The Derivative Time is a parameter that can be adjusted to increase system response
to fast load or reference changes, and to reduce overshoot upon startup. To
eliminate the differential function entirely, set this parameter to 0.00 seconds.
The PID Output Limit (Cn-51, Cn-52) parameter can be used to set the maximum
effect the PID controller will have on the system. It will also limit the PID output
when it is either positive or negative.
Содержание MA7200
Страница 26: ...1 22 ...
Страница 153: ...DISTRIBUTED BY 5100 NORTH IH 35 ROUND ROCK TEXAS 78681 www tecowestinghouse com 03 14 2005 ...