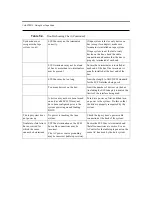
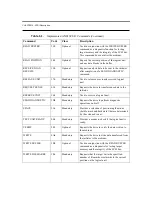
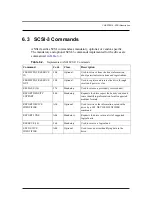
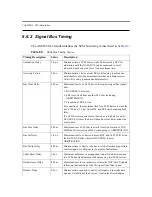
CHAPTER 6: SCSI Description
6.4
Parity
Parity is a method of generating redundant information that can be used to detect
errors in stored or transmitted data.
Data transmitted across the SCSI interface is protected by redundant parity bits:
•
One bit for the 8-bit narrow SCSI implementation
•
Two bits for the 16-bit wide SCSI implementation.
These parity bits detect errors in transmission across SCSI and trigger a resend of
the bad data.
6.5
Signal States
The following paragraphs describe signal values and SCSI IDs.
6.5.1 Signal Values
All signal values are actively driven true (low voltage). Because the signal drivers
are OR-tied, the bus terminator’s bias circuitry pulls false when it is released by
the drivers at every SCSI device. If any device asserts a signal, (for example,
OR-tied signals), the signal is true.
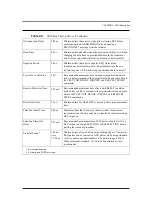
Table 6-3
lists the ANSI-specified and defined
signal sources. Any device can assert RST at any time.
Содержание SDLT220-320 INTEGRATION
Страница 1: ...TANDBERG Super DLTTM Product manual Revision 2 June 2002 432589 01...
Страница 20: ...CHAPTER 1 Introduction...
Страница 34: ...CHAPTER 2 SDLT 220 320 Product Information...
Страница 52: ...CHAPTER 3 Drive Specifications...
Страница 76: ...CHAPTER 4 Installing Your Tape Drive...
Страница 87: ...CHAPTER 5 Using Your Tape Drive Figure 5 1 SDLT 220 and SDLT 320 Front Panels A Comparison SDLT 220 SDLT 320...
Страница 92: ...CHAPTER 5 Using Your Tape Drive...
Страница 104: ...CHAPTER 6 SCSI Description...
Страница 120: ...APPENDIX A SDLT I Tape Cartridge...
Страница 126: ...APPENDIX B DLT IV Tape Cartridge Figure B 4 Tape Cartridges with Damage Visible During Visual Inspection...
Страница 130: ...APPENDIX B DLT IV Tape Cartridge...