Chapter 6
Section 6.5
Implementing the JDBC/ODBC eWay Sample Projects
Building and Deploying the prjJDBC_JCD Sample Project
JDBC/ODBC eWay Adapter User’s Guide
89
Sun Microsystems, Inc.
Steps required to create an Environment:
1
From the Enterprise Designer’s Enterprise Explorer, click the
Environment
Explorer
tab.
2
Right-click the Repository and select
New Environment
. A new Environment is
added to the Environment Explorer tree.
3
Rename the new Environment to
envJDBCProj
.
4
Right-click
envJDBCProj
and select
New > JDBC External System
. Name the
External System
esJDBC.
Click
OK
.
esJDBC
is added to the Environment Editor.
5
Right-click
envJDBCProj
and select
New > File External System
. Name the
External System
esFileClient
. Click
OK
.
esFileClient
is added to the Environment
Editor.
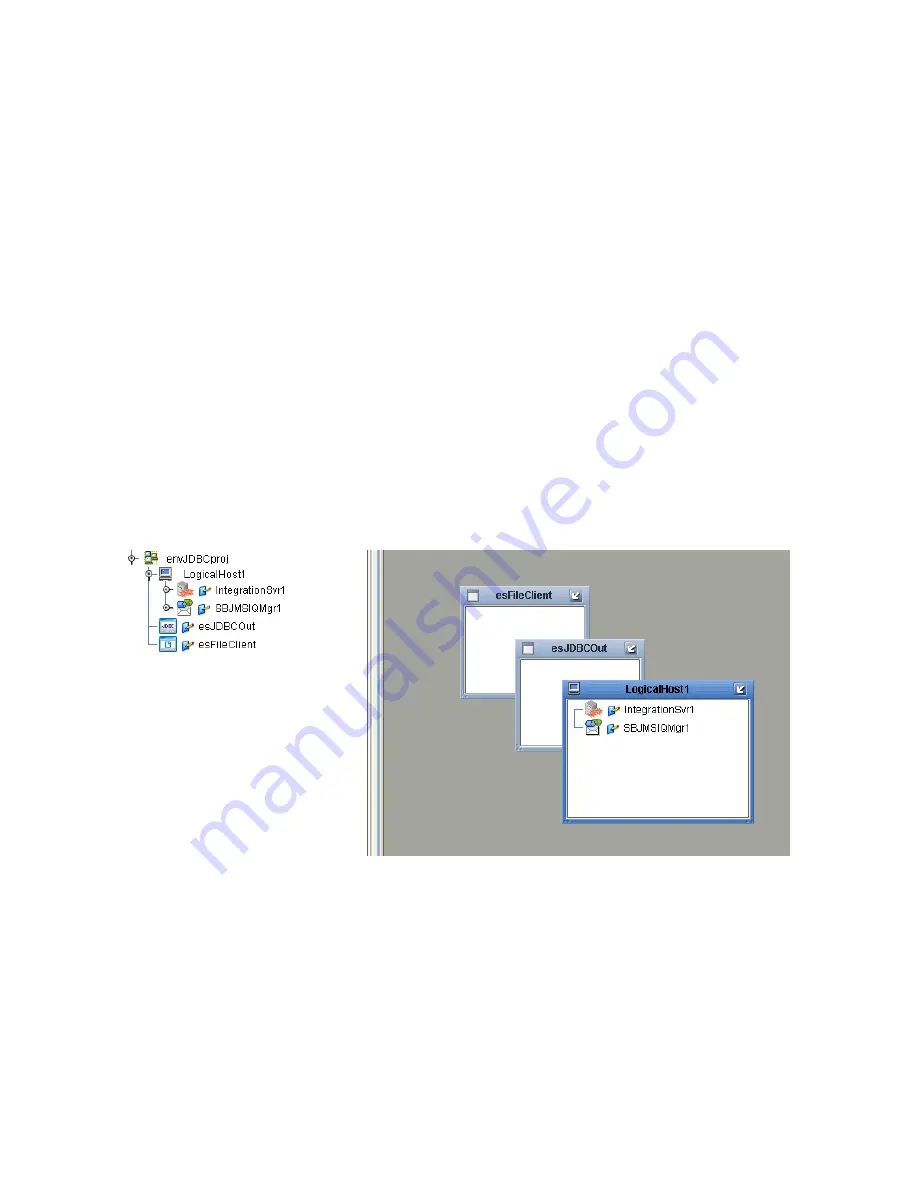
6
Right-click
envJDBCProj
and select
New > Logical Host
. The
LogicalHost1
box is
added to the Environment and
LogicalHost1
is added to the Environment Editor
tree.
7
Right-click
LogicalHost1
and select
New > Sun SeeBeyond Integration Server
. A
new Integration Server (
IntegrationSvr1
) is added to the Environment Explorer tree
under
LogicalHost1
. See Figure 37.
Figure 37
Environment Editor - envJDBCProj
8
Save your current changes to the Repository.
6.5.8
Configuring the eWays
eWays facilitate communication and movement of data between the external
applications and the eGate system. Each Connectivity Map in the
prjJDBC_JCD
sample Project uses three eWays that are represented as nodes between the External
Applications and the Business Process. See Figure 38.