An EyeLink Portable Duo Tutorial: Running an Experiment
©
2016-2017 SR Research Ltd.
53
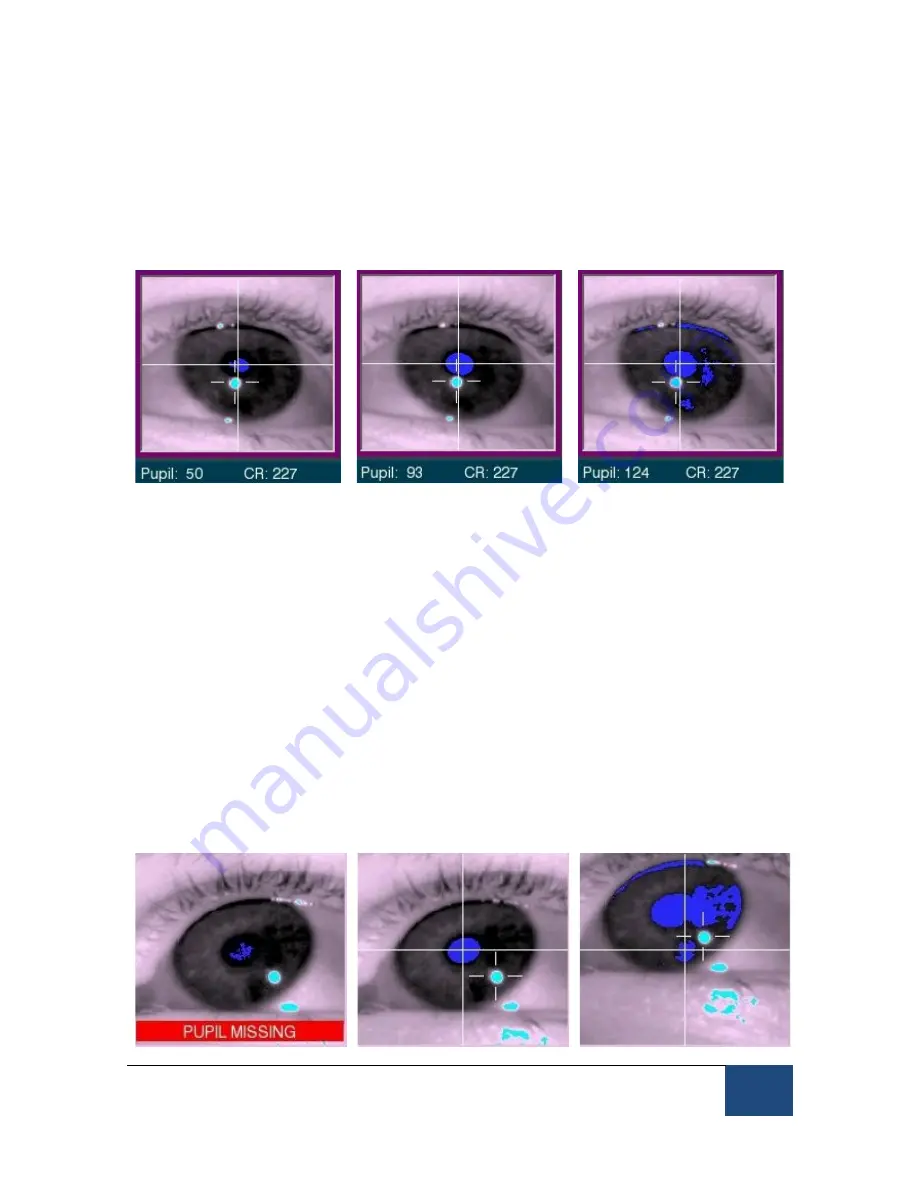
threshold is too low, the blue area will be smaller than the pupil, and the eye
tracker data will be excessively noisy. If the threshold is too high, there will be
shadows at the edges and corners of the eye, especially when the eye is rotated.
Adjust the pupil threshold by using the pupil threshold adjustment buttons or
with the
⇑
and
⇓
keyboard shortcuts: a mnemonic is to think of the
⇑
key as
increasing the blue area, and the
⇓
key as decreasing the blue area.
Threshold Too low: Noisy
Good Pupil Threshold
Threshold too high:
Shadows
Figure 3-7: Symptoms of Poor Pupil Threshold
The Setup display is updated very rapidly, so noise, shadows, etc. will be easily
detected. You can have the participant look at the corners of the monitor, and
watch the pupil image for problems. One common problem is for shadows at the
corners of the eye, which can capture the pupil (see the right panel of Figure
3-8). These may be eliminated by decreasing the threshold with the
⇓
key. Be
careful not to drop the threshold too much, as the pupil thresholding may be
poor at extreme eye positions. The pupil on the Host screen should have a
crosshair drawn around its center, indicating that it has been detected. If a
shadow captures the pupil, or the pupil is severely under-thresholded (as in the
left panel of Figure 3-8), the crosshair will disappear and the pupil will be lost.
On the Host PC, a “Pupil Missing” error will appear in the zoomed eye image.






























