7.4 Page Control Setting
The user can use the page control register to set the type of access to the relevant page. Certain areas of the ERTEC
200 must be implemented with a 32-bit data access in order to ensure data consistency. For other areas, an 8-bit or 16-
bit data access is permitted. The following table shows which ERTEC 200 address areas require 32-bit access.
ERTEC 200 Area
32-Bit Access Required
32-Bit Access
Possible
System control register
X
-
Timer 0 / 1 / 2
x
-
F-counter
x -
Watchdog x
-
IRT register
x
-
SDRAM -
x
KRAM (as user RAM)
-
x
KRAM (Switch RAM)
-
x
Residual APB I/O (UARTs,
SPI, GPIO)
- x
Table 23: Summary of Accesses to Address Areas of ERTEC 200
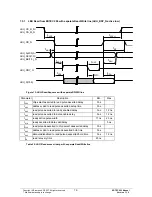
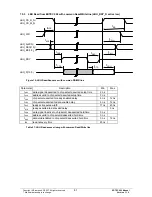
A setting is made in the paging control registers to indicate whether the relevant page area is addressed according to a
16-bit or 32-bit organization. In the case of a page with 16-bit organization, each byte or word access is forwarded to the
AHB bus. In the case of a page with 32-bit organization,
32-bit read access is implemented on the AHB bus when the LOW word is read. In addition, the LOW word is forwarded
and the HIGH word is stored temporarily in the LBU. A subsequent read access to the HIGH word address outputs the
temporarily stored value. This ensures consistent reading of 32-bit data on a 16-bit bus. In the case of 32-bit write
access, the LOW word is first stored temporarily in the LBU area. When the HIGH word is write accessed, a 32-bit
access to the AHB bus is implemented. Byte accesses are forwarded directly to the AHB bus and are therefore not
useful for a 32-bit page.
When the host accesses address areas of the ERTEC 200, a distinction must be made between 16-bit and 32-bit host
processors.
The data width of the variables is defined for a 16-bit host processor. The various compilers implement the accesses in
any order. In the case of a 32-bit access by the user software, it must be ensured that LOW word access to the 32-bit
address area p
In the case of a 32-b
of the host
processo
7.5 Host Acces
When a host a
it access options.
The following a
recedes HIGH word access.
it host processor, the access order is defined by setting the "external bus controller"
r. In this case, the address area access must be assigned as "
Little Endian access."
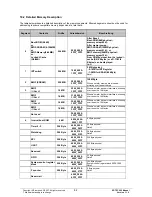
s to the ERTEC200
ccesses the ERTEC 200, it behaves like a 16-bit Little Endian block with 8-bit and 16-b
ccesses are supported:
LBU_BE1_N
LBU_BE0_N
LBU_A0
AHB Access
1 0 0 8-Bit
LOW
0 1 1 8-Bit
HIGH
0 0 0
16-Bit
Rest Not
permitted
Table 24: Host Access to Address Areas of ERTEC 200
Access by the host is asynchronous to the AHB clock of the ERTEC 200. For this reason, it is synchronized with the AHB
clock. The following figures show different read- and write sequences with the timings:
Copyright © Siemens AG 2007. All rights reserved.
78
ERTEC 200 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.1.0