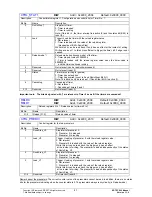
4.7 Synchronous Interface SPI
An SPI interface is implemented in the ERTEC 200. The inputs and outputs of the SPI interface are available as an
alternative function at GPIO port [23:16]. For this purpose, the I/O must be assigned to the relevant inputs and outputs
and the alternative function must be assigned (see GPIO register description). If the SPI interface is used, the pins are
no longer available as standard GPIO. The base frequency for the internal bit rate generation is the 50 MHz APB clock.
The data bit width for read/write access is 16 bits.
The following signal pins are available for the SPI interface on the ERTEC 200.
•
Transmit cable
1
SSPTXD
•
Receive
cable
1
SSPRXD
•
Clock
cable
2
SCLKIN/ SCLKOUT
•
Enables
2
SSPCTLOE/SSPOE
•
SFRs
2
SFRMIN/SFRMOUT
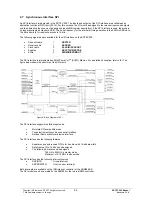
The SPI interface is implemented as ARM Prime Cell
TM
(PL021) Macros. For a detailed description, refer to /6/. The
figure below shows the structure of the SPI macro.
Figure 8: Block Diagram of SPI
The SPI interface supports the following modes:
•
Motorola SPI-compatible mode
•
Texas Instruments synchronous serial interface
•
National Semiconductor microwire interface
The SPI interface has the following features:
•
Separate send and receive FIFOs for 8 entries with 16-bit data width
•
Data frame of 4 to 16 bits can be assigned
•
The following bit rates can be assigned
769 Hz to 25 MHz in master mode
Maximum of 4.16 MHz in slave mode
The SPI interface has the following interrupt sources:
•
SSPINTR
Group
interrupt
•
SSPRORINTR
Overrun error interrupt
Both interrupts are available on the IRQ interrupt controller of the ARM946E-S.
The SPI module can be operated by the ARM946 or the internal DMA controller.
Copyright © Siemens AG 2007. All rights reserved.
54
ERTEC 200 Manual
Technical data subject to change
Version 1.1.0