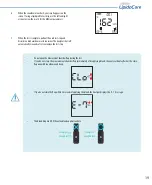
23
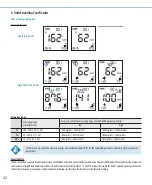
mg/dL
mmol/L
Classification
LDL
<100
<2.59
Optimal
100~129
2.59~3.34
Near optimal/
above optimal
130~159
3.36~4.11
Borderline high
160~189
4.14~4.89
High
≥190
≥4.91
Very high
Total
Cholesterol
<200
<5.18
Desirable
200~239
5.18~6.19
Borderline high
≥240
≥6.22
High
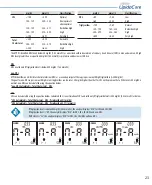
mg/dL
mmol/L
Classification
HDL
<40
<1.03
Low
≥60
≥1.55
High
Triglycerides
<150
<1.69
Normal
150~199
1.69~2.25
Borderline high
200~499
2.26~5.64
High
≥500
≥5.65
Very high
The ATP III identified HDL levels below 40 mg/dL (1.03 mmol/L) as associated with increased risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in men and women. A high
HDL level greater than or equal to 60 mg/dL (1.55 mmol/L) is protective and decreases CHD risk.
HDL
HDL is valid only if Triglyceride level is below 650 mg/dL (7.34 mmol/L).
non-HDL
ATP III identifies non-HDL (total cholesterol minus HDL) as a secondary target of therapy in persons with high triglycerides (≥200 mg/dL).
The goal for non-HDL in persons with high serum triglycerides can be set at 30 mg/dL higher than that for LDL on the premise that a VLDL level ≤30 mg/dL is
normal. non-HDL can be calculated using the equation below.
*non-HDL(calculated) = Total Cholesterol - HDL
LDL
LDL can be calculated using the equation below. Calculated LDL is an estimation of LDL and valid only if Triglyceride level is 400 mg/dL (4.52 mmol/L) or below.
*LDL (calculated) = Total Cholesterol - HDL - (Triglycerides/5) (mg/dL)
*LDL (calculated) = Total Cholesterol - HDL - (Triglycerides/2.17) (mmol/L)
• If Triglyceride level is above 400mg/dL (4.52mmol/L), the analyzer displays "N/A" for LDL and LDL/HDL.
• If Triglyceride level is "Hi", the analyzer displays "N/A" for HDL, LDL, LDL/HDL and non-HDL.
• If HDL level is "Lo", the analyzer displays "N/A" for HDL, LDL, LDL/HDL and non-HDL.
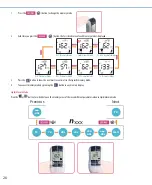
BL
BL
BL
BL
BL
TC/HDL